第十四講:The Cutaneous Senses
出自KMU Wiki
目錄
|
觸覺的重要性
- 最確實的感覺
- 全身最後的防護前哨
- 最強力的人際溝通
- 與發展也有關
觸覺人際溝通
- 社會溝通
- 西方vs東方
- culturally specific
- 西方vs東方
觸覺特性
- Reality(真實)
- complex abilities
- Helen Keller對外界的主要管道
- receptor
- Mechanoreceptors (機械感受器)
Touch qualities
- firmness
- 硬度—用壓的
- shape
- 形狀—尋求軌跡(用姆指與食指)
- smoothness
- 平滑度--滑過表面(用手掌)
sensitivity
- 最早測量
- Max Von Frey (1896)
- 用hair
- 最好lips,fingertips次之
- 最差背(back)腹部(stomach)
- vibrate
- 200Hz最佳
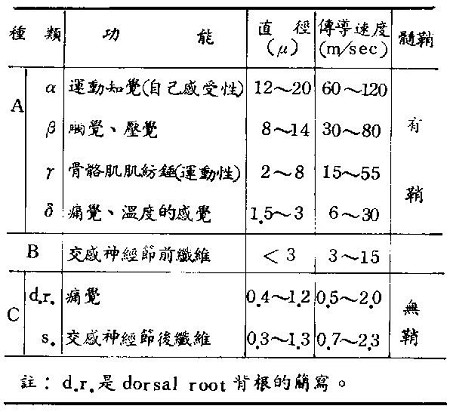
receptor properties接受器特性
- temporal (時間)
- slowly adapting(慢適應) (SA) fibers
- rapidly adapting (快適應)(RA) fibers
- spatial (空間)
- Punctate(點狀) fibers
- Diffuse(擴散)fibers
四種組合
- SA-diffuse
- SA-punctate
- RA-diffuse (PC, Pacinian corpuscle)
- RA-punctate
receptor of touch
- Meissner corpuscles
- Pacinian corpuscles
- Merkel disks
- Ruffini endings
- free nerve endings
Receptors
- 參照第339頁 figure 14.1
- 參照第340頁 figure 14.2
觸覺神經通路
- 參照第340頁 figure 14.3
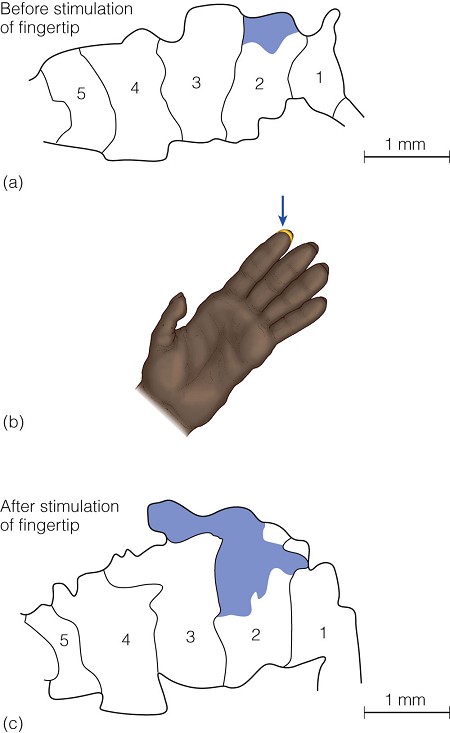
Somatosensory cortex
- 參照第341頁 figure 14.4
homunculus
- 一個小人
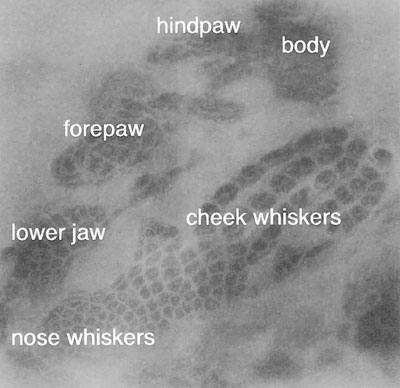
somatosensory cortex
- rat
- 注意whiskers
重覆刺激!
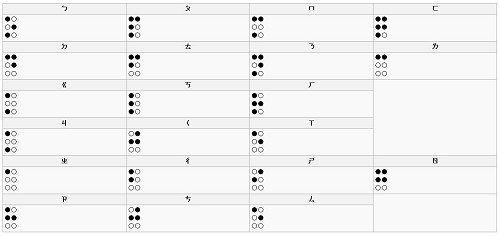
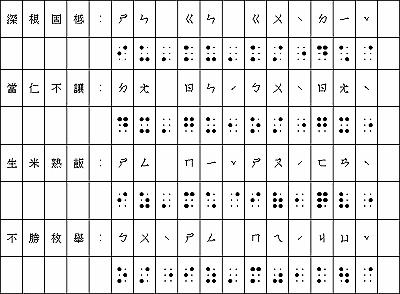
Braille alphabet
- 參照第342頁 figure 14.5
Braille
- Louis Braille在19世紀發明
- Braille好處
- 中文點字
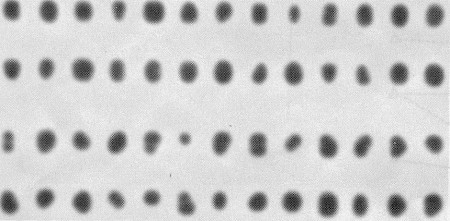
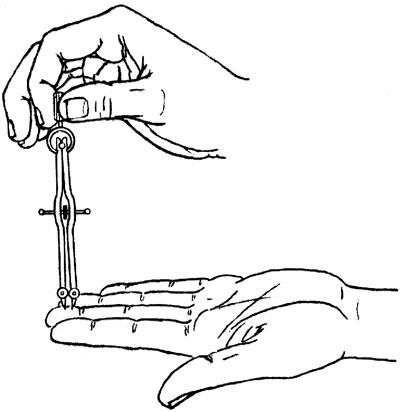
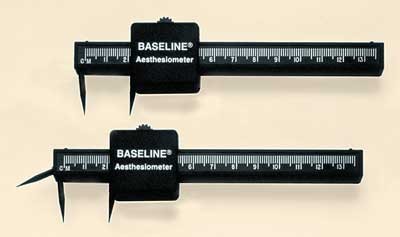
Measuring Tactile Acuity
- 參照第343頁 figure 14.6
Receptor and Tactile Acuity
- 參照第343頁 figure 14.7
acuity
- touch acuity(觸覺解析度)
- two-point thresholds(兩點覺閾)
- two-point threshold
- 在finger <2mm
- forearm (前臂)~30mm
- back (背)~70mm
- Localization(定位)
- Sensitivity(敏感), acuity(解析), localization
Two Point Acuity
- 參照第344頁 figure 14.8
tactile stimulation
- 刺激形式與acuity
Two point threshold
- 參照第344頁 figure 14.9
Receptive field and cortex
- 參照第345頁 figure 14.10
Perceiving Vibration
- 參照第345頁 figure 14.11
Perceiving Texture
- 參照第346頁 figure 14.12
Texture and vibration
- 參照第347頁 figure 14.13
Exploratory Procedures (EPs)
- 參照第349頁 figure 14.14
- Haptics
Physiology of Tactile Object Perception
- 參照第349頁 figure 14.15
Thalamus receptive field
- 參照第350頁 figure 14.16
Receptive field in somatosensory cortex
- 參照第350頁 figure 14.17
Grasp in Parietal cortex
- 參照第350頁 figure 14.18
Tactile attention
- 參照第351頁 figure 14.19
Nociceptive receptors
- 參照第351頁 figure 14.20
Phantom limb
- 參照第352頁 figure 14.21
Gate control model
- 參照第352頁 figure 14.22
gate control theory cont.
- 由於按摩及振動等,Aβ粗纖維受到刺激後,使T細胞興奮,傳導至分支 的同時也使SG細胞興奮,於是到達T細胞前粗纖維和細纖維受到突觸前抑制(pre-synaptic inhibition),因此T細胞興奮受到抑制,不能傳導疼痛。
針灸
- 針灸可能就是對於表皮深部或肌肉深部間的感受器予以刺激,誘使發出一種非痛覺性(即是不具痛覺的)傳導。
- 此種非痛覺性傳導曾興奮Aα型的粗大知覺神經,依門柵控制假說(gate control theory),而可將C型微細神經所傳來的痛覺信息阻遏住。
MYTHS about pain
- acupuncture
- analgesia(止痛)
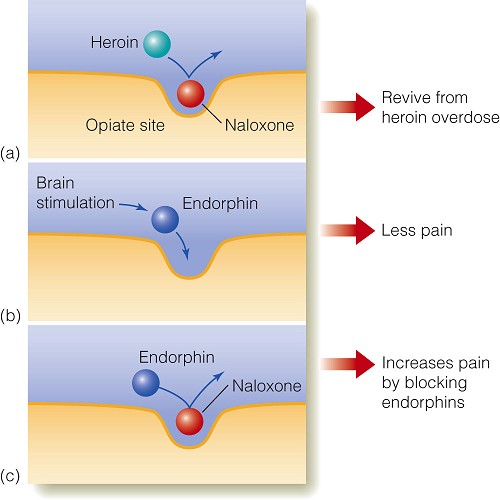
- Endorphins腦內啡
- inducing pain
- pain and weather
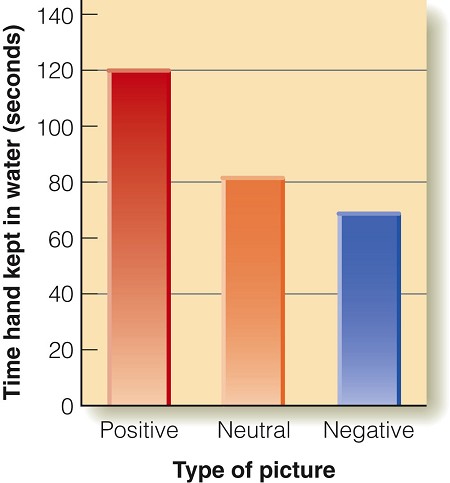
Condition and pain
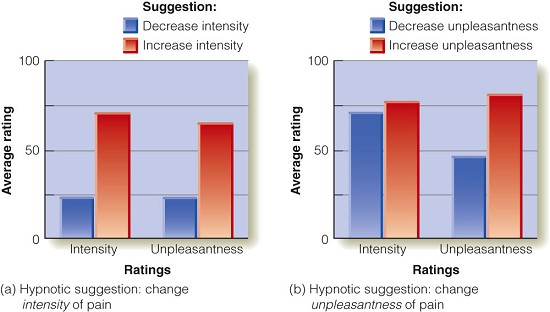
Hypnosis
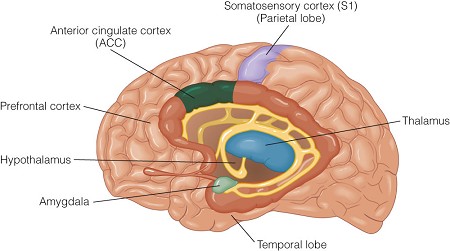
Pain matrix
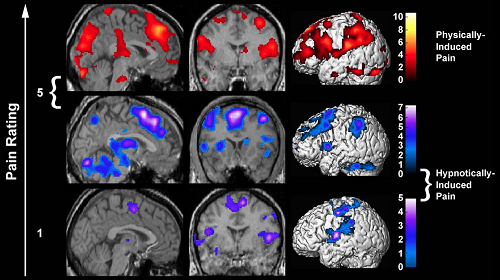
Physical / Hypnosis pain
Chemicals in the Brain
Pain and Placebo
- placebo effect
Effect of Observing
- Keysers et. al. (2004) fMRI
- Meyer et. al. (2011) watching haptic
Empathy ??
- Singer et. al. (2004)
Pain in Social Situation
- Empathy??
- 蠢動含靈皆有佛性,科學家如是證明
- Empathy and Pro-Social Behavior in Rats
- 人腦
- p349 figure14.29
返回知覺心理學