第四講:大腦與視覺
出自KMU Wiki
The Brain and Seeing
- Seeing as an active process
- 我們看東西是被動的嗎?
- 差在那裡?
- 雙可圖形
- 視覺解釋及記憶
- 前面四張圖的結論
- 我們所見不是只有光學影像本身
- 我們用眼睛及再加....來看
- 本章主題就是....
- ....是什麼?
- Optic Nerve
- Optic Nerve示意圖
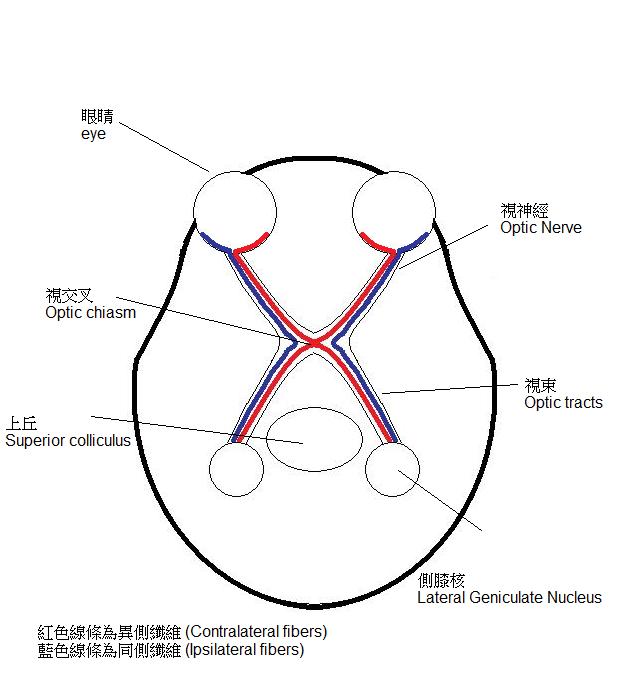
- Optic Nerve(視神經)
- Optic chiasm(視交叉)
- Optic tracts(視束)
- Nerve -> chiasm -> tracts
- 其實都是retina ganglion cells的axon
- 解剖上的不同
- lateral projection(側投射)
- 不是左眼到右腦
- ipsilateral fibers(同側纖維)
- contralateral fibers (異側纖維)
- lateral projection
- Superior colliculus(上丘)
- location
- function
- Multimodal(多感道) input
- 控制眼睛移動。
- receptive field property(特性)
- Phylogenetic(系統發生) – old
- 在低等動物中,上丘已經存在並且是腦中處理視覺的重要部分。在高等動物中,視覺皮層 (Visual cortex) 取代了上丘的地位而成為重要的處理視覺區。雖然如此,有一學說認為上丘是在處理刺激方向有重要作用。
- 有receptive fields—but ill-defined ON OFF
- 對stimulus之where反應,what較不反應
- 結果—guidance of eye movement
- Multisensory cells(多重感覺細胞)
- 組成上丘的細胞除了接收視覺傳來的刺激外,還會接收聽覺傳來的刺激,因它可以接收不同的刺激,所以命名為多感覺細胞。
- Lateral Geniculate Nucleus(側膝核)
- location
- 側膝核位於Thalamus(視丘)中,是它的其中一部分。
- Shape
- 形狀就好像一個彎曲的膝蓋 (Geniculate)
- 側膝核分為六層,由細胞體組成。以細胞體大小分為大細胞層 (Magnocellular layers) 和小細胞層 (Parvocellular layers) 。
- Magnocellular layers
- Layer 1,2 large-cell layers
- Magnus Latin words mean『large』
- Parvocellular layers
- Layer 3,4,5,6 small-cell layers
- Parvus Latin words mean 『small』
- K cells
- Sandwiched between 各layers
- Layers
- 從內到外
- 1,2,3,4,5,6
- 每一層與同側纖維 (Ipsilateral fibers) 或對側纖維 (Contralateral fibers) 連接。
- Maps in LGN
- retinotopic map
- retinotopic maps 中記錄的情況
- receptive fields properties of LGN
- 形狀
- lateral inhibition
- 刺激特性
- color
- all parvocellular
- color opponent (red/green, blue/yellow)
- acuity
- fovea附近敏感度小
- magnocellular敏感度會比parvocellular大
- temporal variation
- K cell?
- multimodal (sound)
- input from superior colliculus
- Possible function of the LGN
- relay of visual information
- Input from Reticular activating system(網狀刺激系統)
- Input from Superior colliculus (K cells)
- shut down vision under rapid eye movement
- Feedback loop from Visual cortex(視覺皮質區)
- ?????
- sorting operation??
- Visual cortex
- occipital lobe(枕葉)
- cortical blindness(皮質視盲)
- Scotomas(暗點)
- Gordon Holmes
- topographic maps(地形圖)
- cortical magnification(皮質放大)
- Structure of visual cortex
- Primary visual cortex
- V1
- Area 17
- Striate cortex
- 1.5~2.0mm thick
- 100million cells in V1 each hemisphere
- 6 layers
- Retinal map
- Topographic
- 80% cells 處理 10%的visual field
- 因此在視野中心的東西在cortical level放大很大
- 週邊視野的東西則變小
- Contralateral(對側) visual field
- 以visual field來分lateral projection
- Function of V1 cell
- orientation selectivity(傾斜選擇性)
- preferred orientation(傾斜的喜好)
- oblique effect傾斜效果
- 有些人不會有效果 meridional amblyopia(經線性弱視 )
- 有些人比較沒有效果,可能與astigmatism有關
- Meridional amblyopia (經線性弱視 )
- Why oblique effect?
- 可能較多horizontal- and vertical-oriented contours in environments
- Neural plasticity(神經可塑性)
- ocular dominance(單眼優勢)
- technic 2-DG
- binocular cells 雙眼細胞
- 其實V1大部分是binocular cells
- binocular disparity 雙眼像差
- Hypercolumn 超柱型組織
- column的組合體
- Hypercolumn by De Valois and De Valois
- orientation
- 受刺激後腦內反應 (請參見color plate 1)
- beyond V1
- 超複雜系統
- parietal stream 顱頂
- dorsal stream 背側
- M pathway
- temporal stream 顳
- ventral stream 腹側
- P pathway
- M
- P
- larger receptive field
- retinotopic map
- position invariance
- feedback loop
- Duality of visual processing 視覺歷程的雙重性
- 1960's
- Ambient(周遭) and focal(中心)
- 1980's
- Parietal stream (where) and temporal stream (what)
- Dorsal stream and ventral stream
- M pathway and P pathway
- P and M
- Schiller and Logothetis (1990) paradigm (with lesion technic)
- Specialized visual area
- 不能主動lesion,只能觀察腦傷病人
- Damage in interior part of the occipital lobe near junction with temporal lobe
- Achromatopsia(無辨色能力)—loss of color vision
- Damage to specitic portions of temporal lobe
- Prosopagnosia(臉型失認)—inablility to face recognition
- Damage in MT
- Akinetopsia(動態失認)—cannot see motion
- relating neurophysiology
- Phosphene(光幻視 )
- see light in complete darkness
- visual hallucination(視幻覺)
- transcranial magnetic stimulation 穿顱磁刺激
- What cortical cells do?
- feature detector(特徵偵測器)? (Barlow, 1972)
- Collaboration 合作
- tilt aftereffect (傾斜後效 )(adaptation(適應))
- tilt aftereffect 可能的解釋
- sparse coding 稀疏編碼
- high order vision
- vision is constructive(視覺是建構的)
- context dependent 情境相依
- integration of local features(整合局部特徵)
回上頁

