第十講:Perceiving Depth and Size
出自KMU Wiki
(修訂版本間差異)
| 在2014年1月14日 (二) 22:47所做的修訂版本 (編輯) Woody (對話 | 貢獻) (→文藝復興) ←上一個 |
在2014年1月14日 (二) 22:50所做的修訂版本 (編輯) (撤銷) Woody (對話 | 貢獻) (→行動與距離) 下一個→ |
||
| 第234行: | 第234行: | ||
| === 行動與距離 === | === 行動與距離 === | ||
| P.254 Figure10.46 | P.254 Figure10.46 | ||
| + | ===Across species== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Frontal / Lateral eye=== | ||
| + | *例如貓、兔 | ||
| + | ===Sonar in Bat=== | ||
| + | ==Infant depth perception== | ||
| + | *Fox et.al. (1980) 利用 RDS 判斷視線 | ||
| + | ===Familiar size in infant=== | ||
| + | *Granrud, Haake, and Yonas (1985) | ||
| + | **利用 preferential reaching | ||
| + | ===Shadows=== | ||
| + | *Yonas and Granrud (2006) | ||
在2014年1月14日 (二) 22:50所做的修訂版本
目錄 |
深度知覺的困難
P.230 Figure10.1
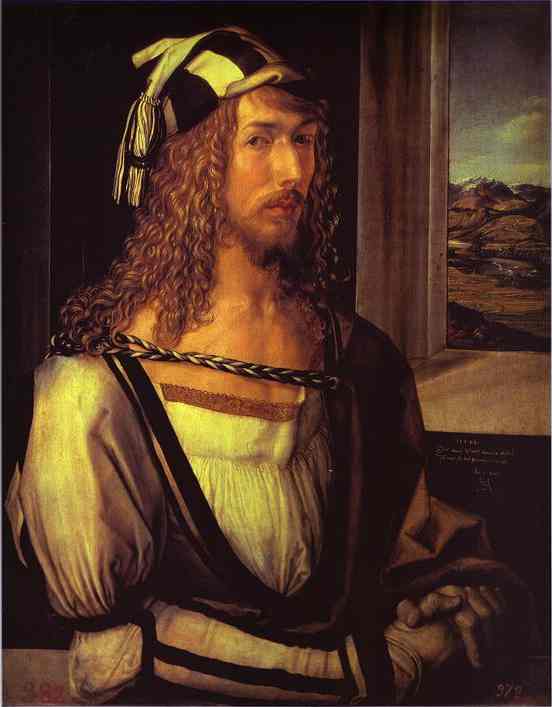
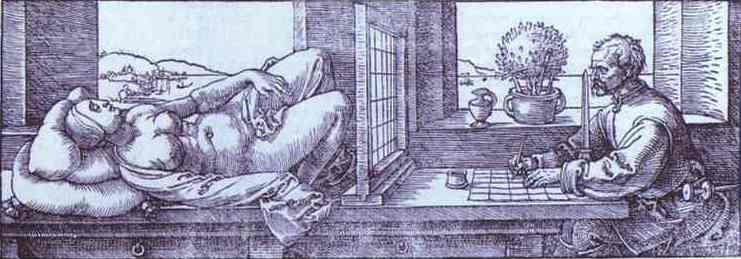
文藝復興
- Albrecht Dürer (阿爾布雷希特·杜勒1471-1528)
文藝復興過程
- 將眼見的呈現在畫中
- 希臘、羅馬時期已到達相當不錯的情況
- 中世紀曾經衰退
- 在前文藝復興年代開始努力恢復
- 文藝復興時確立
- 如前述的Albrecht Dürer
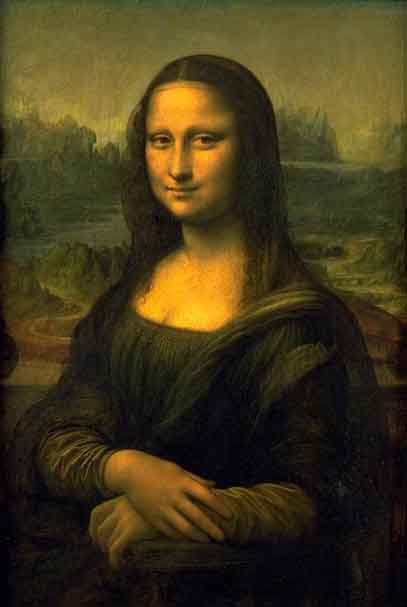
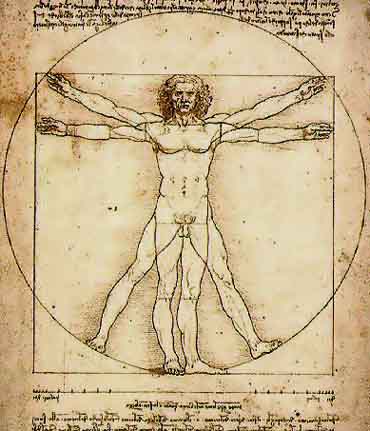
- 及Leonardo da Vinci (李奧納多·達文西)
pre-Renaissance(前文藝復興期)
- 不完全的透視
- Albrecht Windows
- Leonardo作法
- Albrecht Dürer
- 北方文藝復興重要人物
Renaissance(文藝復興)
- 地區
- 以義大利為中心
- 延伸至北方(法蘭西、神聖羅馬帝國...)
- 以及英格蘭
- 影響範圍
- 文學
- 藝術
- 科學
Leonard da Vinci
- 義大利
- 科學家
- 藝術家
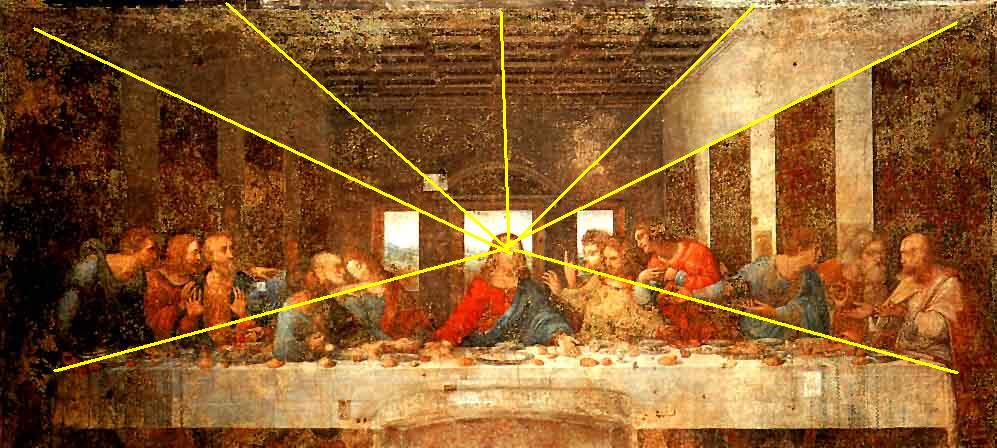
- 最後的晚餐
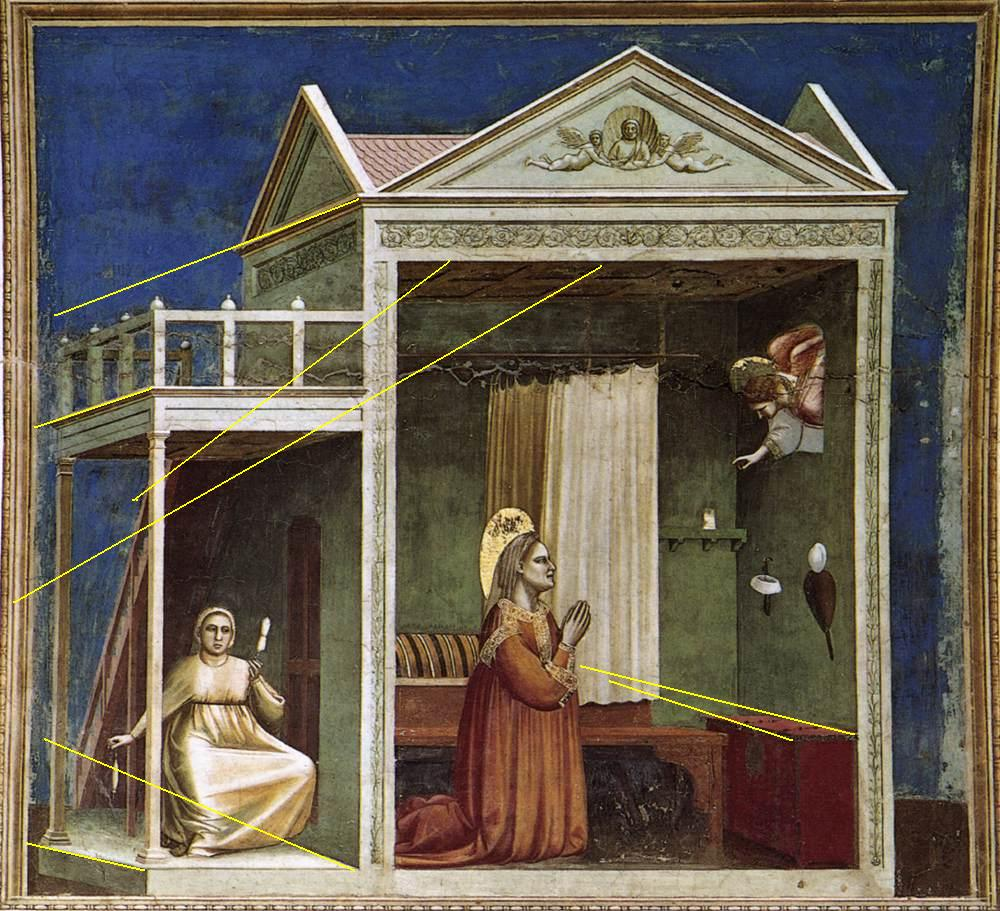
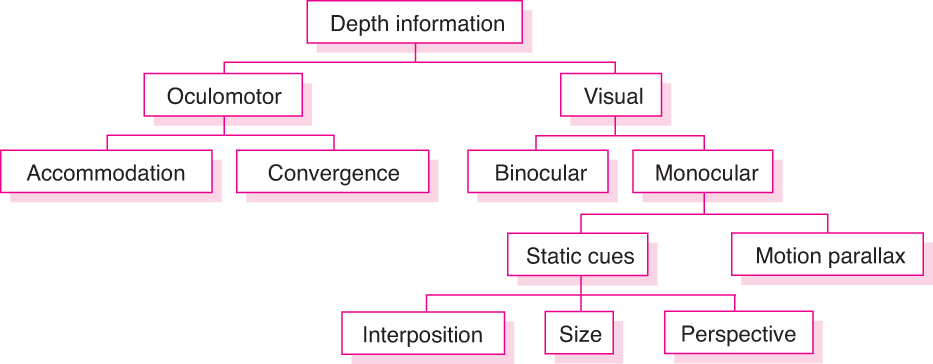
depth cues (深度線索)
- 各類深度線索
Vergence
P.231 Figure10.2
單眼線索
- 圖畫線索
Relative Height
地平線以上與以下
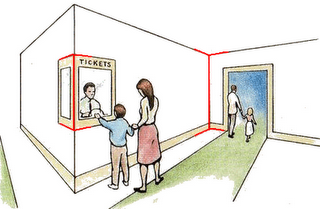
Perspective Convergence
又稱直線透視
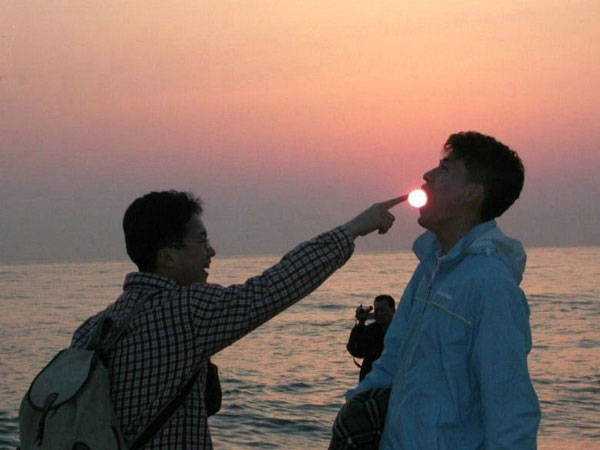
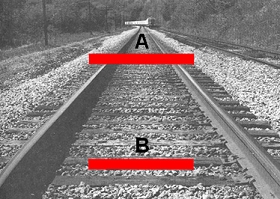
Familiar size
P.232 Figure10.4
Atmospheric perspective
- 空氣透視
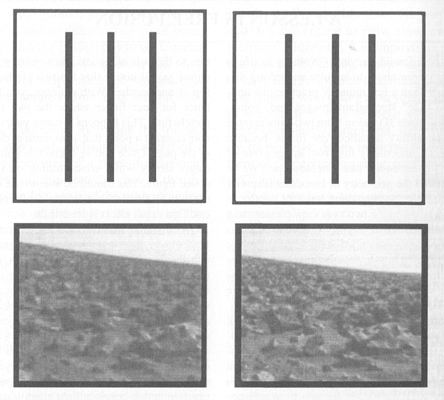
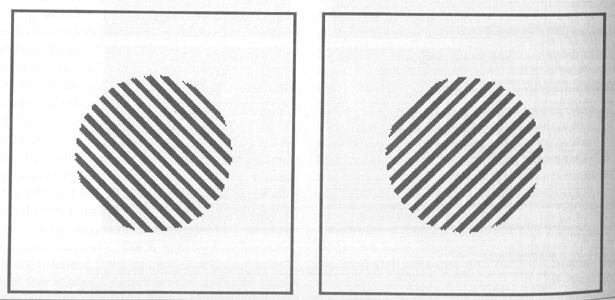
Texture gradient
- 質地遞變
Shadows
- 光線與陰影
shading
- shading and texture
- depth movement
光線方向
- 照相時機
Motion paralla
P.234 Figure10.8
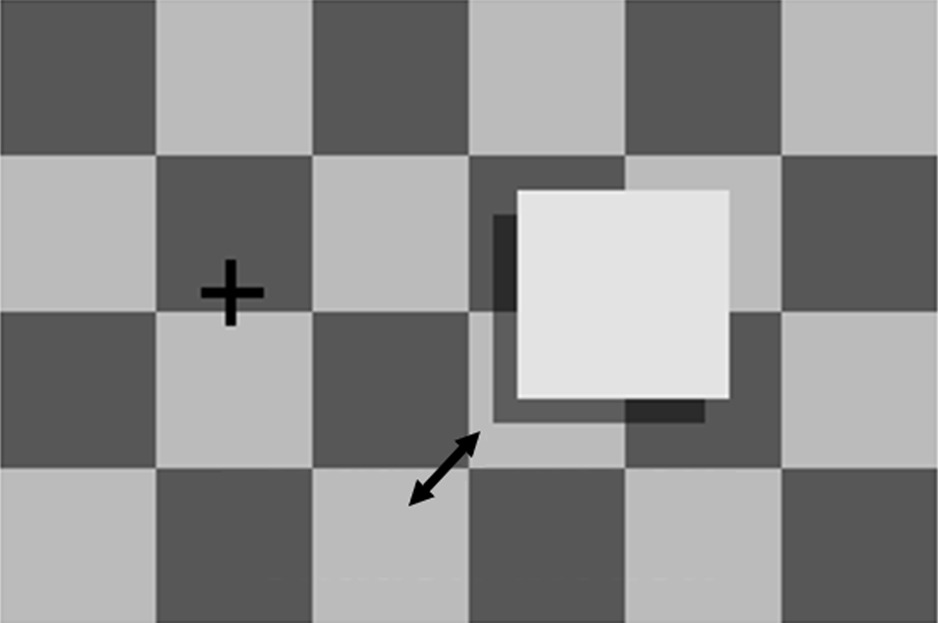
Deletion and Accretion
- 阻檔與解除
Occlusion
- 重疊(近與遠)
Range of Depth Cues
- 各線索有效性不同
雙眼位置
- 閉上右眼,手指放在遠方物體上。手指不動換右眼來看
2D vs 3D
影像的形成
Corresponding points
Horopter
binocular disparity
Stereoscope(立體鏡)
- Wheatstone 19世紀發明
- 使用鏡子
- ViewMaster
- 使用菱鏡及透鏡
- 紅綠濾鏡
- 偏光鏡
- Autostereogram(單張式立體圖)
3D圖形
- 左、右眼圖
- 簡易實體鏡
實體鏡
- 三種類型
- 3D movies 古
- 3D movies 新
- 帶動者 Avatar
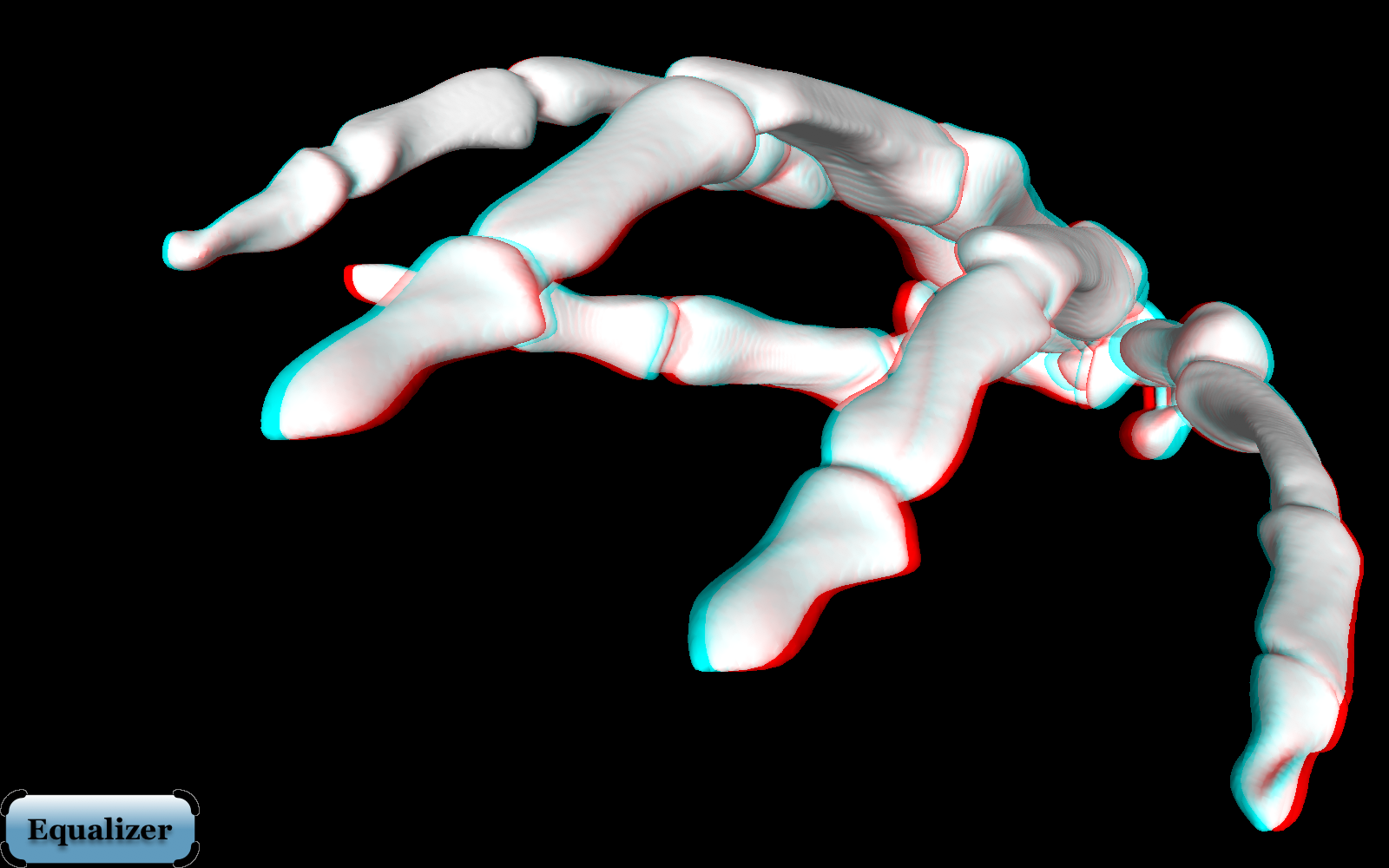
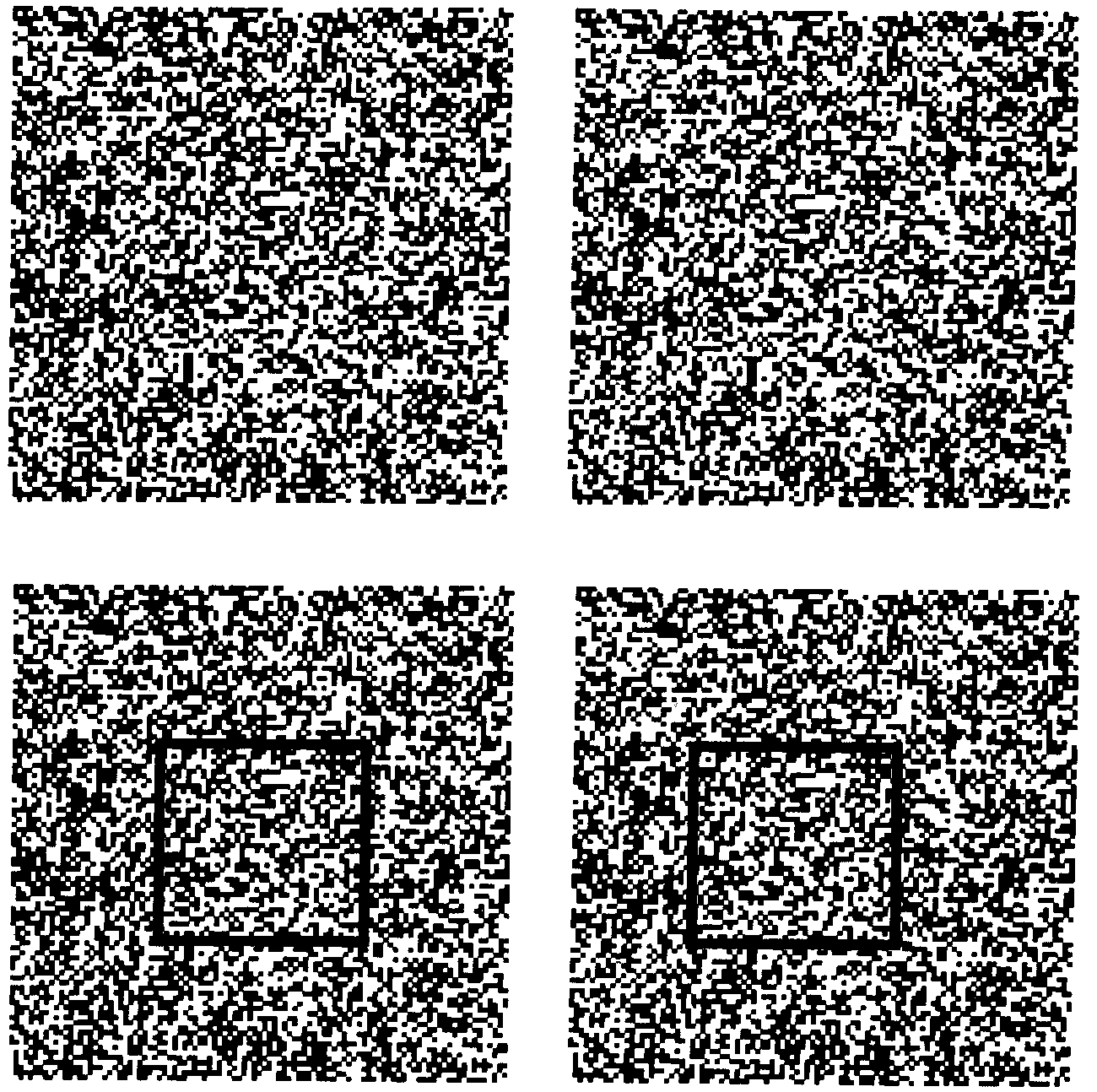
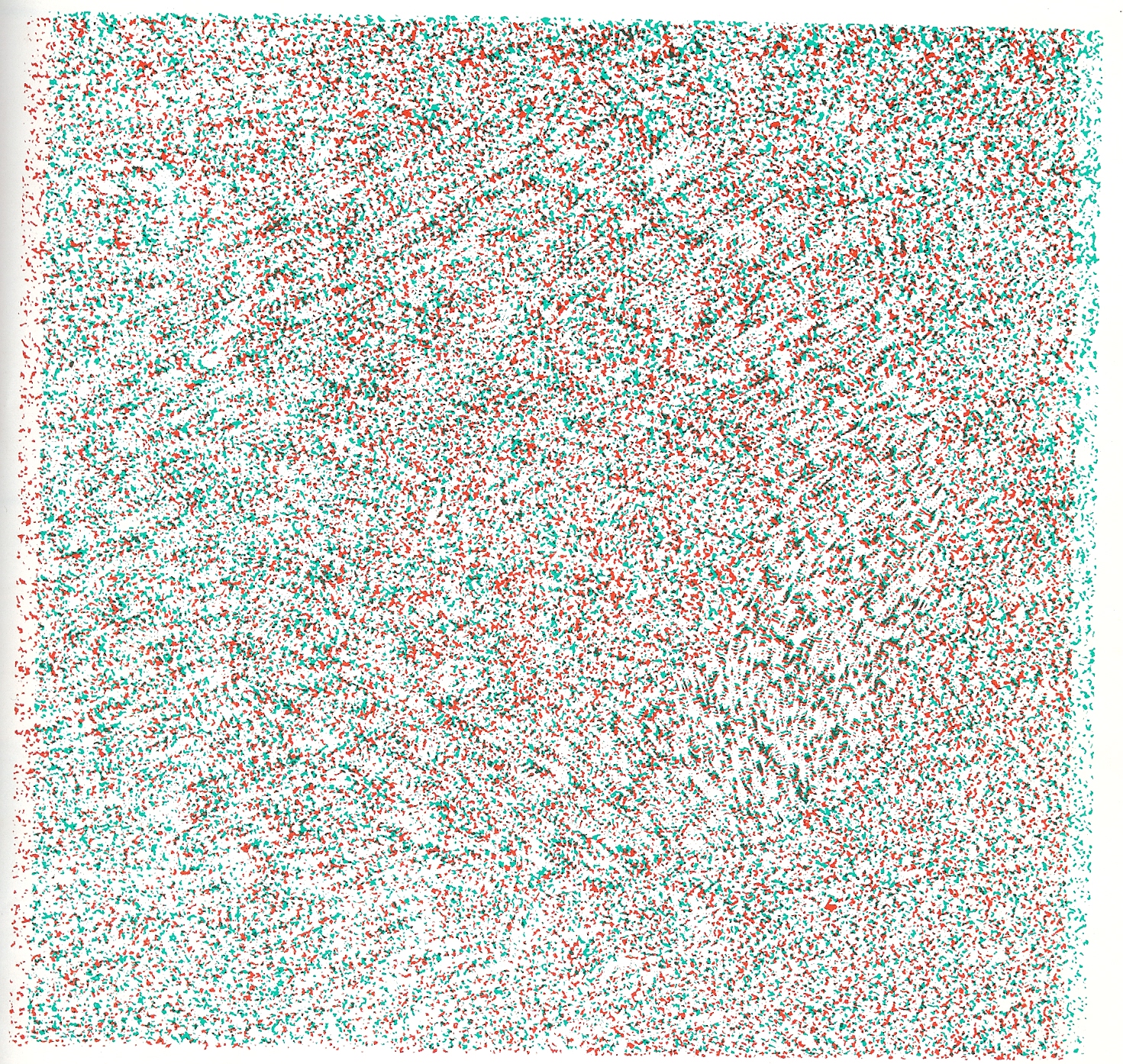
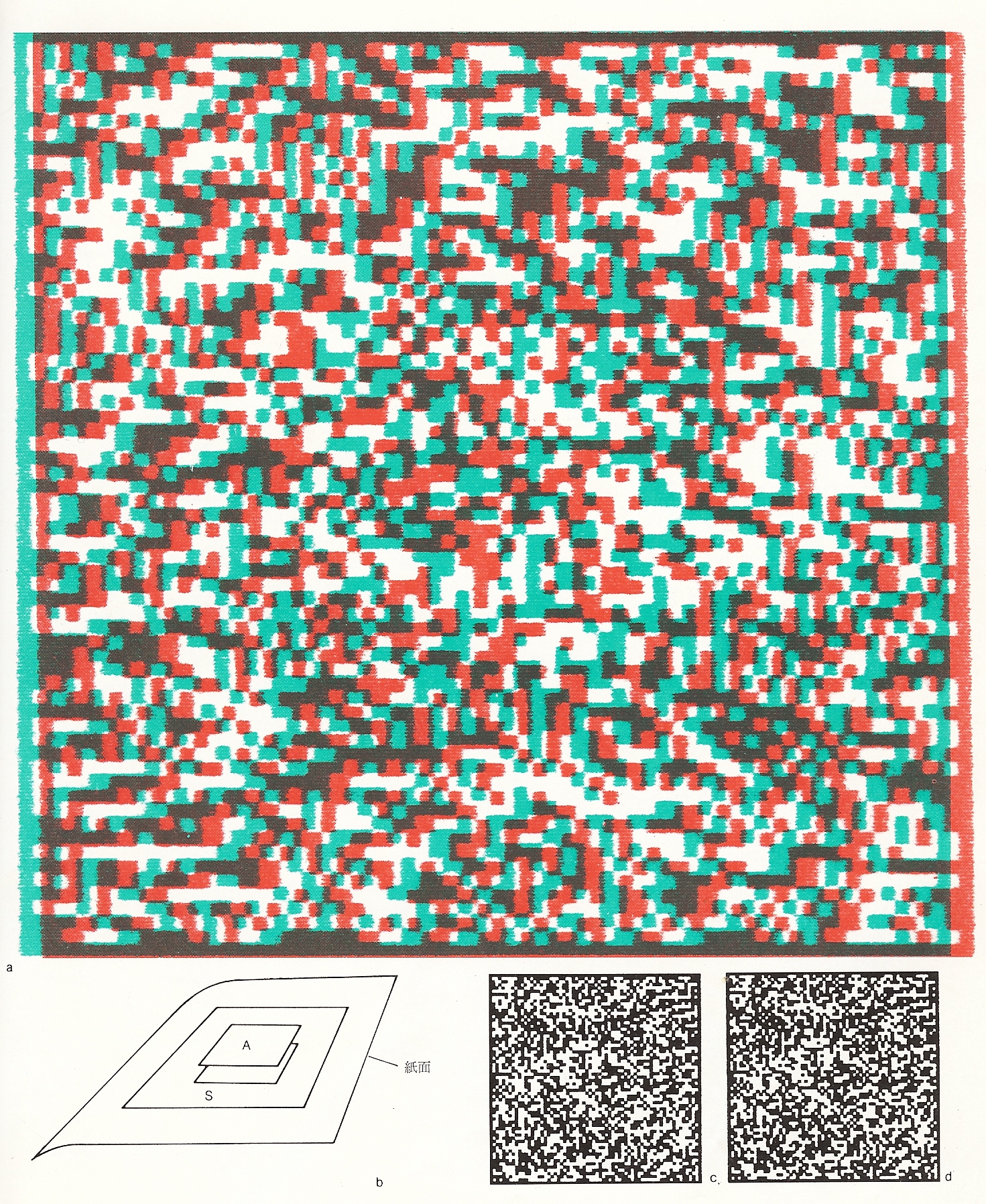
RDS (Random-dot Stereogram)
- Autostereogram
- “Magic Eye”box 8.2
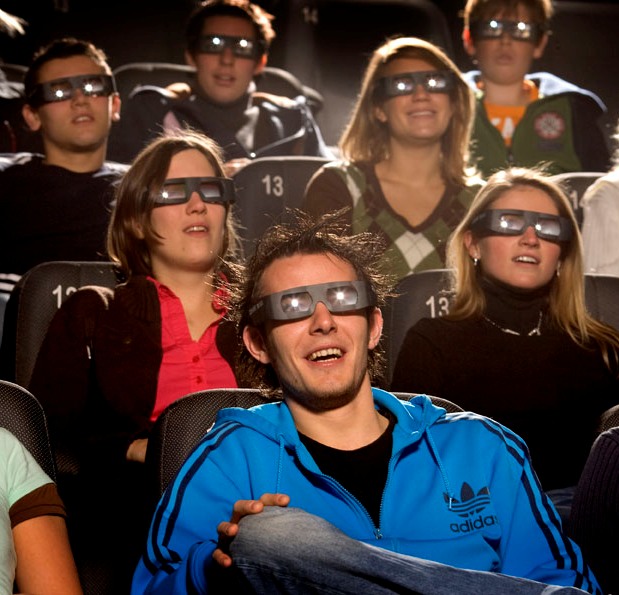
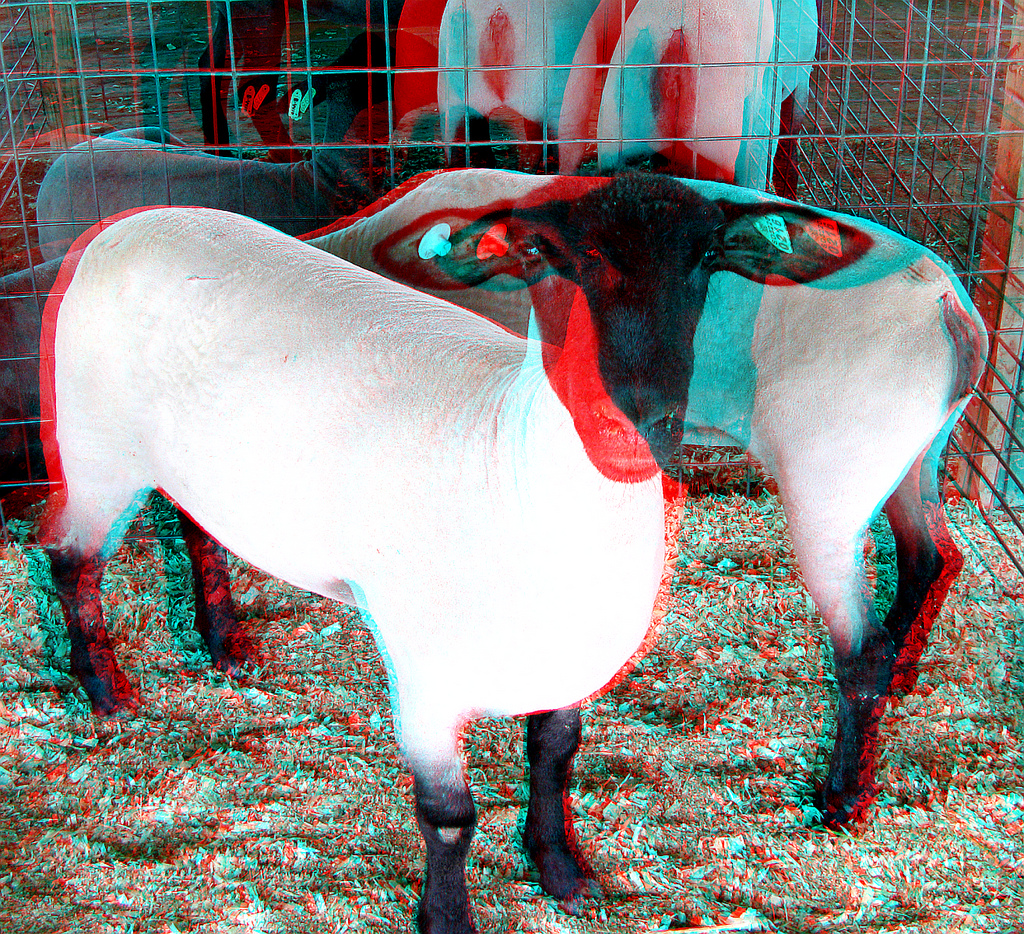
- Anaglyph(紅綠立體圖)
- 要帶紅綠眼鏡(左眼紅、右眼綠)
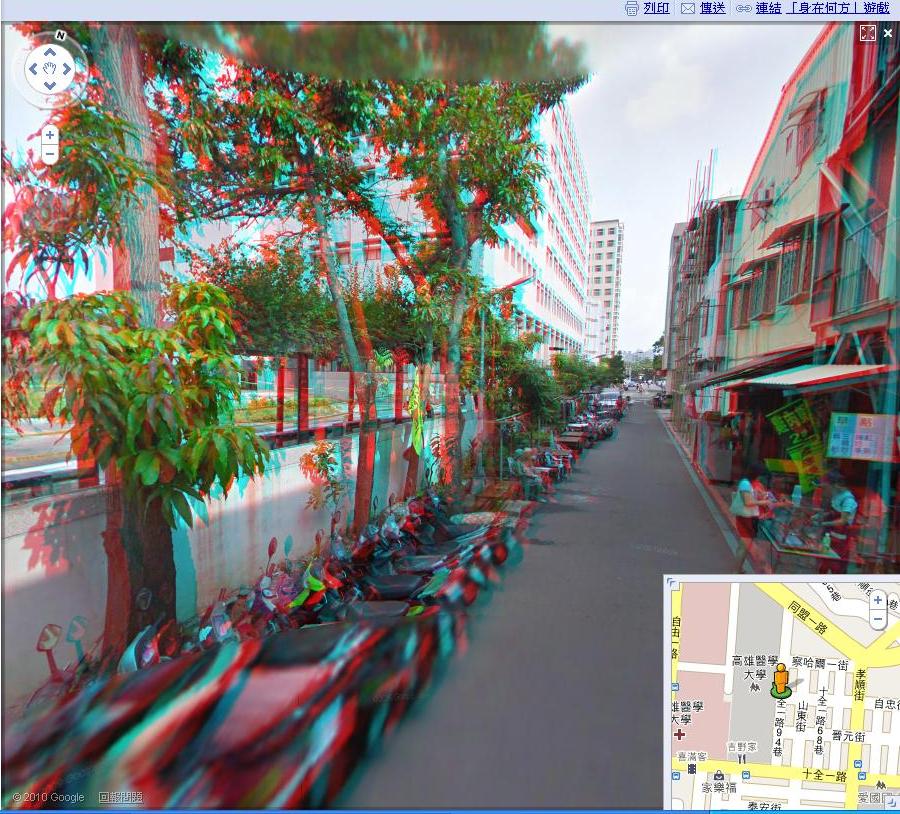
- Google 街景也可以看3D
- 拉下街景小人後,街景上按右鍵
- 選3D mode on
- 拉下街景小人後,街景上按右鍵
- random-dot stereogram(隨機點立體圖)
- Bela Julesz (1959)
- RDS anaglyph
- 受試者看到的
- RDS anaglyph
- 要戴紅綠眼鏡( 接下來兩張要左綠、右紅)
SF & stereopsis
- RDS原空間頻率
- low spatial frequency
- high spatial frequnecy
- left=low/right=high -> rivalry
binocular rivalry(雙眼競爭)
- 雙眼競爭 box8.3
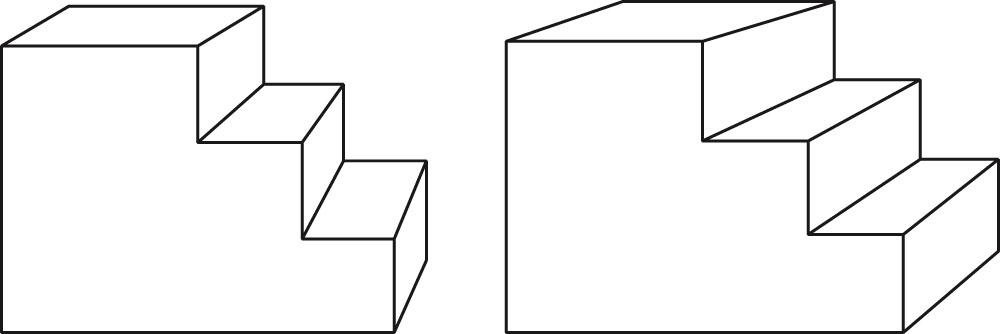
da Vinci stereopsis(達文西立體圖)
- amodal completion(非形式補整)
Neural basis
- disparity-selective cells(像差偵測細胞)
- Stereoblindness(立體盲)
- strabismus (斜視)
- diplopia (複視)
- convergence insufficiency(輻奏不協調)
對gradient反應之細胞
- 刺激大腦可以使深度知覺改變
知覺歷程中之關係
- 刺激、生理、知覺
Whiteout
P.244 Figure10.26
Holway and Boring (1941)
P.244 Figure10.27
Visual angle
P.245 Figure2.28 請回去想一想視角怎麼算?
- 大致大小
P.245 Figure2.29
- 單眼觀察
- 遠近的trick
Holway and Boring (1941)結果
P.246 Figure2.31
- Visual angle again :p
P.247 Figure2.32
Size constancy
- Size distance invariance
Emmert's law
P.248 Figure10.33
- size-distance scaling S = K (R X D)
- familiar size
P.248 Figure10.34
- texture gradient and size
P.248 Figure10.35
Muller-Lyer illusion
P.249 Figure10.36
- Gregory (1966)的解釋
- 以大小恆常來解釋
- 否證之一
P.250 Figure10.38
- 否證之二
P.250 Figure10.39
Conflicting Cues Theory
- Day (1989, 1990)
Ponzo illusion
- 可以用大小與距離關係來解釋
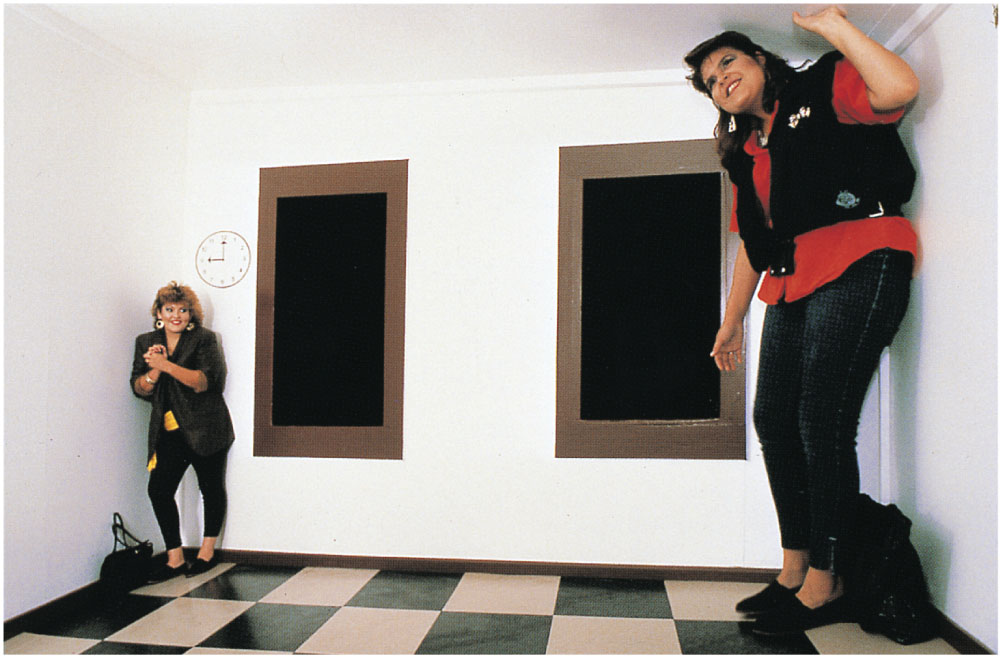
Ames room
- Ames room 解釋
P.252 Figure10.43
moon illusion
P.252 Figure10.44
- moon illusion之一種解釋
P.253 Figure10.45
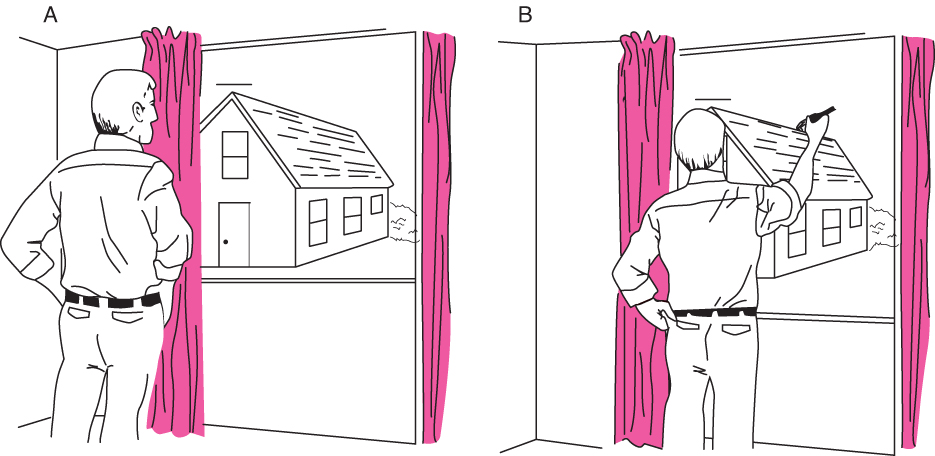
行動與距離
P.254 Figure10.46
=Across species
Frontal / Lateral eye
- 例如貓、兔
Sonar in Bat
Infant depth perception
- Fox et.al. (1980) 利用 RDS 判斷視線
Familiar size in infant
- Granrud, Haake, and Yonas (1985)
- 利用 preferential reaching
Shadows
- Yonas and Granrud (2006)