心理實驗法第十講:Control
出自KMU Wiki
(修訂版本間差異)
| 在2007年11月9日 (五) 09:08所做的修訂版本 (編輯) Sakurai (對話 | 貢獻) ←上一個 |
在2007年11月9日 (五) 09:09所做的修訂版本 (編輯) (撤銷) Sakurai (對話 | 貢獻) 下一個→ |
||
| 第103行: | 第103行: | ||
| === 實驗基本架構 === | === 實驗基本架構 === | ||
| - | [[ | + | [[Image:Iv-dv.PNG]] |
| === How to control? === | === How to control? === | ||
在2007年11月9日 (五) 09:09所做的修訂版本
Control
在科學的實驗作什麼?
- 觀察對比(contrasts)
- 實驗組與控制組
- 各獨變項間
- 推論(inferences)
- 根據由所觀測的對比結果
- 推論獨變項的影響
- 對比
- 有/無
- 如spallanzani狗懷孕的實驗
- 實驗組—過濾精蟲(即無精蟲)
- 控制組—未過濾精蟲(即有精蟲)
- 量之不同
- 如Ehrenfreund & Badia(1962)
- 剝奪成95% vs 85%
- 獎勵45mg vs 260mg
- 量如何調整?
- 課本75頁敘述
- 比較尼龍網球拍與KeVlar球拍的彈性
- 兩個相差1gm的網球
- 一個網球、一個鉛球
Control
- 兩種variables要control
- Confounding variables
- 使其影響力下降
- Independent variables
- 增加contrasts(對比)
- Confounding variables
推論
- 根據結果來推論
- 結果就是因獨變項而來的變化
- 如spallanzani狗懷孕的實驗
- 實驗組—過濾精蟲(即無精蟲)--未懷孕
- 控制組—未過濾精蟲(即有精蟲)--懷孕
- 對比造成的結果
- 就是原因與結果的關係
結果
- 實驗的結果
- 需要實徵性(empirisism)
- 即需穩定、可重覆
- 且自受試者(對象)直接取得
- 結果理想上
- 可觀察或測量得到
- 但....如何觀察或測量?
Measurement
- 看不見怎麼辦?
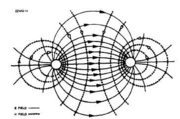
- Electromagnetic field
- Finely machined iron particles
- Charged electrode
- Observe iron particles
- Get the mathematical models
- 手機如何知道有電磁輻射?
Electromagnetic Fields
- 看不到,但是存在
- 在利用適當的「控制」使他顯現
- 鐵粉 v.s. 鋁粉
- 有電 v.s. 無電
- 作出一結論
- or 右圖
[
- Scientific observation
- Observing contrasts
- 電磁場 有電 v.s. 無電
- In a controlled environment
- 均勻鐵粉,在實驗室中
- Or in nature
- Observation form a system of knowledge
- 改變電極、改變電壓
Models
- System of knowledge
- 可以整理複雜的現象
- 以簡御繁
- 可以預測
- 可以提供後來研究者檢驗—可否證性
- 可以作合理的解釋
Scientific inference
- 推論—有一份證據說一份話
- 所以要跟據obervation推論
- Observation之validity受subjects之特性影響
- 因此要實驗組與控制組「相當」
- 例如:一實驗用「鐵粉」,另一實驗用「鋁粉」測電磁場,不同不是因電磁場理論不對!
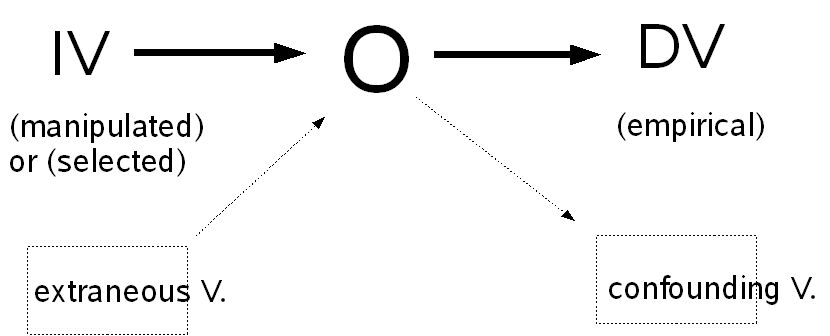
實驗基本架構
How to control?
- Control confounding V.
- Holding condition constant
- 要注意只要控制相關的
- 如:visual illusion的實驗
- 受試者之 color of eye, height, athletic ability, knowledge of Swiss mountain cheese....無關)
- 受試者之eyesight, illumination(有關,要控制)
- 如:visual illusion的實驗
- 要控制所有的?
- 要找到所有相關的extraneous V.?
- Don't chase ghosts p.77
- Good experimental design is characterized by careful attention to the control of real extraneous variables and the investigation of important topics......
- 要注意只要控制相關的
Lorge(1930) Massed practice v.s. Distributed practice
- 工具
- 鏡描
- 分組(IV)
- a.連續20次練習
- b.每次休息1分鐘
- c. 每次休息1天
- DV 完成速度 c>b>a
Holding Conditions Constant
- Loarge(1930)實驗為例
- 三組中唯一不同的是:練習間休息時間
- 其他恆定
- 練習次數(練習與練習間,即休息時間,不會有機會讓他們練習)
- 作業難易度一定
Subject variables
- Subject variable-subject variable confound
- There is always a danger that it is related in some systematic manner to another subject variables.
- p.91 high-authoritarian with IQ
- High-authoritarian group 在學習complex task時表現不佳
- 但authoritarian 與IQ有負相關
Control again
- 兩種variables要control
- Confounding (Extraneous) variables
- 使其影響力下降
- 增加data的穩定度
- Independent variables
- 增加contrasts(對比)
- 增加data的差異性
- Confounding (Extraneous) variables
Models again
- System of knowledge
- 可以整理複雜的現象
- 以簡御繁
- 可以預測
- 可以提供後來研究者檢驗—可否證性
- 可以作合理的解釋