第八講:Perceiving Motion
出自KMU Wiki
(修訂版本間差異)
| 在2013年11月13日 (三) 20:55所做的修訂版本 (編輯) Woody (對話 | 貢獻) (→運動知覺) ←上一個 |
在2013年11月13日 (三) 21:16所做的修訂版本 (編輯) (撤銷) Woody (對話 | 貢獻) (→運動知覺) 下一個→ |
||
| 第5行: | 第5行: | ||
| *自己也在動 | *自己也在動 | ||
| [[Image:x002.jpg]] | [[Image:x002.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===運動知覺之課本的圖=== | ||
| + | 就是前兩張 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===運動知覺可給意義=== | ||
| + | *Heider and Simmel (1944) | ||
| + | *只是大三角形、小三角形及圖形在移動的動畫(兩分半鐘),但可以講出故事 | ||
| ===不幸病歴=== | ===不幸病歴=== | ||
| + | |||
| *Figure 8.2 (p.179) | *Figure 8.2 (p.179) | ||
| *Ms. L.M. | *Ms. L.M. | ||
| 第15行: | 第23行: | ||
| **故事(口述)+ 影片 | **故事(口述)+ 影片 | ||
| - | + | ==hidden bird== | |
| *[http://www.psychology.pomona.edu/hiddenbird/ 網站] | *[http://www.psychology.pomona.edu/hiddenbird/ 網站] | ||
| + | |||
| ===視線方向與物體辦識=== | ===視線方向與物體辦識=== | ||
| 第27行: | 第36行: | ||
| **[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Gathering_For_Gardner_Dragon.ogv 動畫] | **[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Gathering_For_Gardner_Dragon.ogv 動畫] | ||
| - | + | ==real motion== | |
| *真實運動 | *真實運動 | ||
| [[Image:x005.jpg]] | [[Image:x005.jpg]] | ||
| 第46行: | 第55行: | ||
| **我們能不能分辨真實與錯覺運動? | **我們能不能分辨真實與錯覺運動? | ||
| **錯覺? | **錯覺? | ||
| + | ===Apparent motion=== | ||
| + | *Gestalt Psychology 啟始的地方 | ||
| ===其他運動相關的錯覺=== | ===其他運動相關的錯覺=== | ||
| 第56行: | 第67行: | ||
| *Wagon-wheel effect | *Wagon-wheel effect | ||
| **車輪會反轉(?)[http://www.michaelbach.de/ot/mot_wagonWheel/index.html 影片一] [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Propeller_strobe.ogv 影片二] | **車輪會反轉(?)[http://www.michaelbach.de/ot/mot_wagonWheel/index.html 影片一] [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Propeller_strobe.ogv 影片二] | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===似動運動之應用=== | ||
| - | *Figure 8.5(b) (p.181) | ||
| - | **LED廣告 | ||
| - | **跑馬燈 | ||
| - | **電視動畫 | ||
| - | **.... | ||
| ===Induced motion=== | ===Induced motion=== | ||
| - | * | + | *動者通常是小的東西 |
| **風大的夜晚,雲動很快,看久了覺月亮在走 | **風大的夜晚,雲動很快,看久了覺月亮在走 | ||
| **[http://psychlab1.hanover.edu/Classes/Sensation/induced/ 測試網站] | **[http://psychlab1.hanover.edu/Classes/Sensation/induced/ 測試網站] | ||
| **如果在三張圖中可以看到不同程度(或是看不到)induced motion,請回饋給作者 | **如果在三張圖中可以看到不同程度(或是看不到)induced motion,請回饋給作者 | ||
| ***網頁最下面有郵件位置 | ***網頁最下面有郵件位置 | ||
| - | ***[KrantzJ@Hanover.Edu e-mail] | ||
| *另一種induced motion (attention induce) | *另一種induced motion (attention induce) | ||
| **看影片TseVideo1.mov | **看影片TseVideo1.mov | ||
| **注意白或黑層紅點閃現的位置會不同 | **注意白或黑層紅點閃現的位置會不同 | ||
| - | **[http:// | + | ***[http://illusionoftheyear.com/2011/attention-induced-motion-displacement/ 原始網址] |
| + | |||
| + | ===似動運動之應用=== | ||
| + | *Figure 8.5(b) (p.181) | ||
| + | **LED廣告 | ||
| + | **跑馬燈 | ||
| + | **電視動畫 | ||
| + | **.... | ||
| ===運動後效=== | ===運動後效=== | ||
| *motion aftereffects MAE | *motion aftereffects MAE | ||
| *waterfall illusion | *waterfall illusion | ||
| - | **figure 8.6 ( | + | **figure 8.6 (a), (b)� |
| - | + | ||
| **[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Illusion_movie.ogg 運動後效產生圖形] | **[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Illusion_movie.ogg 運動後效產生圖形] | ||
| ***注視圖中心至少20秒 | ***注視圖中心至少20秒 | ||
| 第87行: | 第96行: | ||
| ===真實與似動運動腦內表現=== | ===真實與似動運動腦內表現=== | ||
| - | * | + | *前頁圖說明: |
| **控制情境中兩個光點同時呈現,真實運動情境中一個光點來回運動,似動情境中兩個光點先後呈現。圖中藍色表示控制組激發的腦區,紅色表示由真實運動所激發的腦區,而黃色表示由似動運動所激發的腦區。結果可發現,真實運動和似動運動激發的區域有很大的重疊。 | **控制情境中兩個光點同時呈現,真實運動情境中一個光點來回運動,似動情境中兩個光點先後呈現。圖中藍色表示控制組激發的腦區,紅色表示由真實運動所激發的腦區,而黃色表示由似動運動所激發的腦區。結果可發現,真實運動和似動運動激發的區域有很大的重疊。 | ||
| 第94行: | 第103行: | ||
| *二、被觀察者在空間中移動,觀察者的視線跟著被觀察者;此時被觀察者在網膜上的影像是不變的,但觀察者仍可知覺到被觀察者移動(圖8.8b)。 | *二、被觀察者在空間中移動,觀察者的視線跟著被觀察者;此時被觀察者在網膜上的影像是不變的,但觀察者仍可知覺到被觀察者移動(圖8.8b)。 | ||
| *三、觀察者本身在空間中移動,空間中所有物體的影像在觀察者的網膜上是移動的,但觀察者知覺到的是一個靜止的空間(圖8.8c)。 | *三、觀察者本身在空間中移動,空間中所有物體的影像在觀察者的網膜上是移動的,但觀察者知覺到的是一個靜止的空間(圖8.8c)。 | ||
| - | |||
| ===optic array=== | ===optic array=== | ||
| *global optic flow vs local disturbance in optic array | *global optic flow vs local disturbance in optic array | ||
| + | ==何時感受「運動」?== | ||
| - | === | + | ===接受器層次的運動偵測=== |
| + | *以最簡單側抑制來說明 | ||
| ===網膜運動偵測假想圖=== | ===網膜運動偵測假想圖=== | ||
| *事實上往右下方運動的線段,也會激發一個對於正右方運動敏感的視覺細胞。解決這個問題的方式就是整合許多細胞的反應以得全貌,medial temporal cortex | *事實上往右下方運動的線段,也會激發一個對於正右方運動敏感的視覺細胞。解決這個問題的方式就是整合許多細胞的反應以得全貌,medial temporal cortex | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===身體動作、眼動、像動=== | ||
| + | *Corollary Discharge Theory | ||
| + | *IDS image displacement signal | ||
| + | *MS motor signal | ||
| + | *CDS corollary discharge signal | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===CD theory=== | ||
| + | *(a)與(b),當網膜影像位置改變,發出IDS。比較器發出影像移動的資訊。(c)MS(動眼訊號)讓眼睛移動,使得網膜影像位置也改變,發出IDS。但MS同時發出CDS,使比較器不會發出影像移動的資訊。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===有空試試之材料=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===有空試試的情境=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===下課就可以玩的=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Real-motion neuron== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *前圖說明 | ||
| + | **細胞在眼睛不動、物體運動時反應(圖8.23a),但當眼睛轉動而物體不動時卻不反應(圖8.23b)。由於這兩物種情況在網膜上的投影是相同的,因此此類細胞應該也考量了眼球運動的訊息,並針對真實運動的物體反應 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Newsome et al. (1989)=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Newsome VS Hubel and Wiesel=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===microstimulation in MT=== | ||
| ===Aperture problem 1=== | ===Aperture problem 1=== | ||
| + | |||
| ===Aperture problem 2=== | ===Aperture problem 2=== | ||
| + | |||
| ===解決aperture problem相關腦區=== | ===解決aperture problem相關腦區=== | ||
| + | |||
| ===解決aperture problem的關鍵=== | ===解決aperture problem的關鍵=== | ||
| *端點 | *端點 | ||
| 第118行: | 第157行: | ||
| **[http://web.mit.edu/persci/demos/Motion&Form/demos/border-own/border-own.html fig. 18] BORDER OWNERSHIP | **[http://web.mit.edu/persci/demos/Motion&Form/demos/border-own/border-own.html fig. 18] BORDER OWNERSHIP | ||
| - | == | + | ==Motion and human body== |
| - | + | *可能與不可能 | |
| - | + | **(b)在極短ISI | |
| - | + | **(c)較長ISI | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | * | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | * | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | * | + | |
| - | * | + | |
| ===Biological Motion=== | ===Biological Motion=== | ||
| 第185行: | 第202行: | ||
| ===Implied motion=== | ===Implied motion=== | ||
| *Hokusai (北齋) | *Hokusai (北齋) | ||
| + | *動感!! | ||
| *Freyd (1983) | *Freyd (1983) | ||
| 第190行: | 第208行: | ||
| **representational momentum | **representational momentum | ||
| - | + | *Freyd (1983) | |
| + | **判斷一樣不一樣,(b)最難 | ||
| ===Reed and Vinson (1996)=== | ===Reed and Vinson (1996)=== | ||
| *representational momentum | *representational momentum | ||
在2013年11月13日 (三) 21:16所做的修訂版本
目錄 |
運動知覺
- 自己之外在動
- 自己也在動
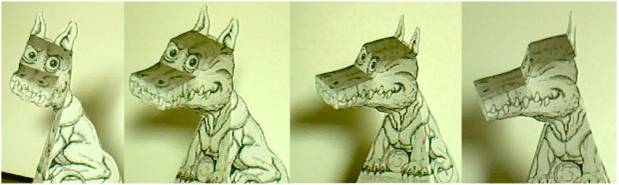
運動知覺之課本的圖
就是前兩張
運動知覺可給意義
- Heider and Simmel (1944)
- 只是大三角形、小三角形及圖形在移動的動畫(兩分半鐘),但可以講出故事
不幸病歴
- Figure 8.2 (p.179)
- Ms. L.M.
- damage in posterior portions of brain
- Akinetopsia
- cannot see movement
- 故事(口述)+ 影片
hidden bird
視線方向與物體辦識
- Figure 8.4 (P.180)
- 另一例
real motion
- 真實運動
Apparent motion
- illusory motion
- phi phenomenon
Troxler's effec
- 另外一種運動錯覺
- 一個值的深思的問題
- 我們能不能分辨真實與錯覺運動?
- 錯覺?
Apparent motion
- Gestalt Psychology 啟始的地方
其他運動相關的錯覺
- Filling-in illusion
- 模糊的邊界會擴散
- Motion-induced blindness
- 高亮度的刺激因週遭運動而消失
Induced motion
- 動者通常是小的東西
- 風大的夜晚,雲動很快,看久了覺月亮在走
- 測試網站
- 如果在三張圖中可以看到不同程度(或是看不到)induced motion,請回饋給作者
- 網頁最下面有郵件位置
- 另一種induced motion (attention induce)
- 看影片TseVideo1.mov
- 注意白或黑層紅點閃現的位置會不同
似動運動之應用
- Figure 8.5(b) (p.181)
- LED廣告
- 跑馬燈
- 電視動畫
- ....
運動後效
- motion aftereffects MAE
- waterfall illusion
- figure 8.6 (a), (b)�
- 運動後效產生圖形
- 注視圖中心至少20秒
- 馬上去看靜止且有東西的地方
真實與似動運動腦內表現
- 前頁圖說明:
- 控制情境中兩個光點同時呈現,真實運動情境中一個光點來回運動,似動情境中兩個光點先後呈現。圖中藍色表示控制組激發的腦區,紅色表示由真實運動所激發的腦區,而黃色表示由似動運動所激發的腦區。結果可發現,真實運動和似動運動激發的區域有很大的重疊。
想像以下情境
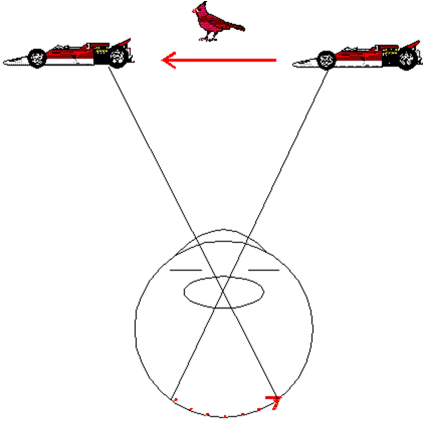
- 一、被觀察者在空間中移動,而觀察者本身不動,觀察者可知覺到被觀察者移動 (圖8.8a)。
- 二、被觀察者在空間中移動,觀察者的視線跟著被觀察者;此時被觀察者在網膜上的影像是不變的,但觀察者仍可知覺到被觀察者移動(圖8.8b)。
- 三、觀察者本身在空間中移動,空間中所有物體的影像在觀察者的網膜上是移動的,但觀察者知覺到的是一個靜止的空間(圖8.8c)。
optic array
- global optic flow vs local disturbance in optic array
何時感受「運動」?
接受器層次的運動偵測
- 以最簡單側抑制來說明
網膜運動偵測假想圖
- 事實上往右下方運動的線段,也會激發一個對於正右方運動敏感的視覺細胞。解決這個問題的方式就是整合許多細胞的反應以得全貌,medial temporal cortex
身體動作、眼動、像動
- Corollary Discharge Theory
- IDS image displacement signal
- MS motor signal
- CDS corollary discharge signal
CD theory
- (a)與(b),當網膜影像位置改變,發出IDS。比較器發出影像移動的資訊。(c)MS(動眼訊號)讓眼睛移動,使得網膜影像位置也改變,發出IDS。但MS同時發出CDS,使比較器不會發出影像移動的資訊。
有空試試之材料
有空試試的情境
下課就可以玩的
Real-motion neuron
- 前圖說明
- 細胞在眼睛不動、物體運動時反應(圖8.23a),但當眼睛轉動而物體不動時卻不反應(圖8.23b)。由於這兩物種情況在網膜上的投影是相同的,因此此類細胞應該也考量了眼球運動的訊息,並針對真實運動的物體反應
Newsome et al. (1989)
Newsome VS Hubel and Wiesel
microstimulation in MT
Aperture problem 1
Aperture problem 2
解決aperture problem相關腦區
解決aperture problem的關鍵
- 端點
aperture problem實驗
- Josh McDermott and Edward H. Adelson Dept. of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, MIT
Motion and human body
- 可能與不可能
- (b)在極短ISI
- (c)較長ISI
Biological Motion
- 發現者 Gunnar Johansson University of Uppsala Sweden 1973
Biological Motion特徵
- point-light motion小燈運動
- biological motion 優在
- occurs automatically自動發生
- < 200msec.
- even color is changed顏色改變也發生
- young infants 初生嬰兒也會
- 看影片
Biological motion腦內位置
- Grossman and Blake (2001)
- 利用Biological and scrambled motion
- STS (Superior temporal sulcus)
- FFA (Fusiform face area)
- biological motion 較優
- EBA (Extrastiate body area)
- 兩者沒差
Grossman and Blake實驗材料
影片 biological motion and scrambled light
測試STS
- 利用TMS (Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation)
- 跨顱磁刺激儀
- Grossman et al.(2005)
Grossman et al. (2005)材料
- (a) biological motion
- (b) scrambled motion
- (c) biological motion + noise 加了線條
- (d) biological motion + noise 實際影像
Implied motion
- Hokusai (北齋)
- 動感!!
- Freyd (1983)
- 受試者會記得見過圖的「下一刻」的樣子
- representational momentum
- Freyd (1983)
- 判斷一樣不一樣,(b)最難
Reed and Vinson (1996)
- representational momentum
Implied motion 腦內表現
- fMRI 記錄 in MT