心理實驗法第七講:factorial design
出自KMU Wiki
(修訂版本間差異)
| 在2013年4月7日 (日) 11:35所做的修訂版本 (編輯) Mi (對話 | 貢獻) (→ 3 Subject variables) ←上一個 |
在2013年4月7日 (日) 11:37所做的修訂版本 (編輯) (撤銷) Mi (對話 | 貢獻) (→ 4 Wheeler & Fiske (2005) 2 X 3) 下一個→ |
||
| 第149行: | 第149行: | ||
| ** Interaction!! | ** Interaction!! | ||
| - | ==== | + | ==== Case study 4 cont. 1 ==== |
| - | * p | + | * 共變 |
| + | ** 共同影響結果的因素(有語病 :p ) | ||
| - | + | * 例如: | |
| - | + | *** 權威性格與智商是共變的 | |
| - | * | + | *** 若研究權威性格高低與問題解決結果 |
| - | ** | + | *** 沒有處理智商問題,我們會不知是智商影響問題解決的結果還是性格? |
| - | * | + | |
| - | ** | + | |
| - | * | + | |
| - | * | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| ==== 5 code and cognitive process ==== | ==== 5 code and cognitive process ==== | ||
在2013年4月7日 (日) 11:37所做的修訂版本
目錄 |
Factorial design
- 隨著時代進步,心理學的方法也進步
- 但心理學想問的問題本質沒有變
- 探討人類心理與行為背後存在的...
- 以前所有問題都只能問最簡單的地方
- 現在有能力問更多
- 為什麼要問更多?
實驗的目的
- Cause-and-effect relationships
- Deprivation -> hungry
- Conflict -> anxiety
- 但人的行為/心理現象通常不是只有一個原因造成
- 高速公路標示辨識為例
- 什麼因素會影響高速公路標示辨識?
- 光線
- 認字能力(韓文標誌看得懂嗎?)
- 意識狀態(如24小時未睡)
- 吃藥或喝酒
- ......
- 不只一個原因影響
- 高速公路標示辨識為例
多因子設計
- 多因子設計(factorial design)
- 例如
- 父母育兒具敵意且過度干涉 -> 小孩退縮
- 若再加上忽略小孩 -> 小孩反社會
- 有些問題勢必兩項或以上的因素在一起才會發生
- 例如
Case study 1
Ehrenfreund and Badia (1962)
- 目的:老鼠在不同剝奪量和獎賞量下表現
- Factor 1 剝奪量
- 95% / 85% ad lib (free-feeding) weight
- Factor 2 獎賞量
- 45mg / 260mg food pellet
- Factor 1 剝奪量
- Dependent variable
- 5 feet跑道中間2 feet的速度
- 控制
- Ad lib weight
- 自然狀態下的體重
- 因為每一隻老鼠的體重進食量不一,因此控制剝奪量本身對於個別動物的影響不同
- 量中間段的速度
- 因為起跑段與終點段的變化比較大
- Ad lib weight
- 結果
- 6-1
- Factors, variables and levels
- Case study 1 為 2X2之factorial design
- Factor 1 為剝奪量
- 有2 levels 之variables
- 即high and low deprivation
- Factor 2 為獎賞量
- 亦有2 levels 之 variable
- 即high and low incentive
- 最多有幾個factor?
- 平常的用語,Factors有時說成variables但一般不會反過來
- Factors與variables組合
- High deprivation – high incentive
- High deprivation – low incentive
- Low deprivation – high incentive
- Low deprivation – low incentive
- 2X2 = 4種組合
- 如果2X2X3 = 12種組合
Measuring attitude
- 態度的測量
- 問卷調查
- 你贊成增加給窮人的社會褔利支出嗎?->19%
- 你贊成增加給窮人的社會救助支出嗎?->63%
- 問卷調查中抽樣的三個層次
- 實體抽樣
- 問題之抽樣
- 受訪者回答之抽樣
- 問卷調查
Case study 2 Cognitive dissonance theory (Festinger,1957)
- Attitude change occur in high-dissonance condition
- Linder, Cooper, and Jones(1967)
- 2X2 factorial design
- Task 寫一篇支持控制言論自由的文章(原本為反對的人)
- Factor 1 選擇(有無告知實驗參與者可不可以有選擇)
- Factor 2 獎賞 $.5 / $2.5
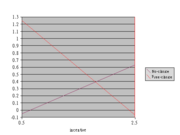
- 結果2
pic.6-2
| Choice | Incentive | |
| $.5 | $2.5 | |
| No-choice | -0.05 | 0.63 |
| Free-choice | 1.25 | -0.07 |
- 繪圖
- p.57 figure4.1
pic.6-3
- Analysis of variance
pic.6-4
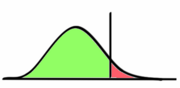
Statistically significant
- 'αlevel'
- .05代表20次有一次by chance顯著
- 'p value'
- 犯type I error 的機率
pic.6-6
- 作圖的重要性
- Case study 1之圖
pic.6-7
Case study 3 Subject variables
- Chi(1978)
- A variables -> recall digits / chess pieces
- B variables -> children / adults
- 結果
- 西洋棋:小孩記得平均9.3,大人則5.9
- 數字:小孩記得平均6.1,大人則7.8
- Interaction!!
Case study 4 cont. 1
- 共變
- 共同影響結果的因素(有語病 :p )
- 例如:
- 權威性格與智商是共變的
- 若研究權威性格高低與問題解決結果
- 沒有處理智商問題,我們會不知是智商影響問題解決的結果還是性格?
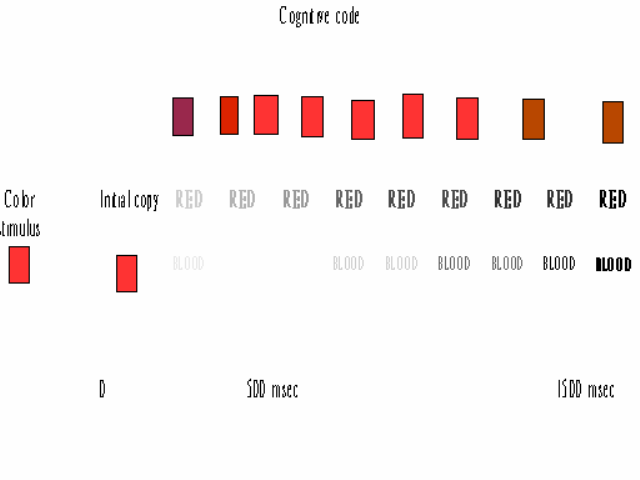
5 code and cognitive process
- “code” record in memory (Posner等人)
- Solso and Short (1979)
- 步驟
- 呈現「色板」
- 間隔後出現第二刺激
- 實驗參與者以按鍵反應「合不合」
- 記錄實驗參與者反應時間(reaction time)
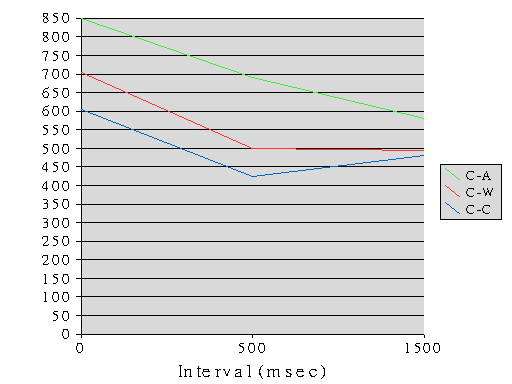
- Complex factorial design
- Factor 1 (type of relationship)
- Color to associate / color to word / color to color
- Factor 2 ( delay between stimulus)
- 0msec. / 500msec. / 1500msec.
- Factor 3 (match or mismatch)
- 3 X 3 X 2
- Case study 5 figure
- Figure 4.5
Mental chronometry
- 實驗結果如p.63 figure 4.5
- Solso and Short的解釋如p.64 figure 4.6
-
- 由reaction time 推測內在歷程
- 利用tachistoscope (T-scope)
- Forced-choice procedure
- Within subject
- Model for case study 5
- Figure 4.6