第四講:大腦與視覺
出自KMU Wiki
(修訂版本間差異)
| 在2010年10月20日 (三) 07:48所做的修訂版本 (編輯) Xiaopiao (對話 | 貢獻) (→The Brain and Seeing) ←上一個 |
當前修訂版本 (2011年10月6日 (四) 01:40) (編輯) (撤銷) Fivesix27 (對話 | 貢獻) (→The Brain and Seeing) |
||
| (2個中途的修訂版本沒有顯示。) | |||
| 第1行: | 第1行: | ||
| - | == The | + | == The Visual Cortex and Beyond == |
| * Seeing as an active process | * Seeing as an active process | ||
| 第16行: | 第16行: | ||
| *** ....是什麼? | *** ....是什麼? | ||
| - | * Optic Nerve | + | === 今天講「腦」《P.74 Gigure4.1》 === |
| + | **訊息自網膜節細胞離開視網膜 | ||
| + | **進入腦 | ||
| + | **LGN -> visual cortex | ||
| + | **視覺經驗 | ||
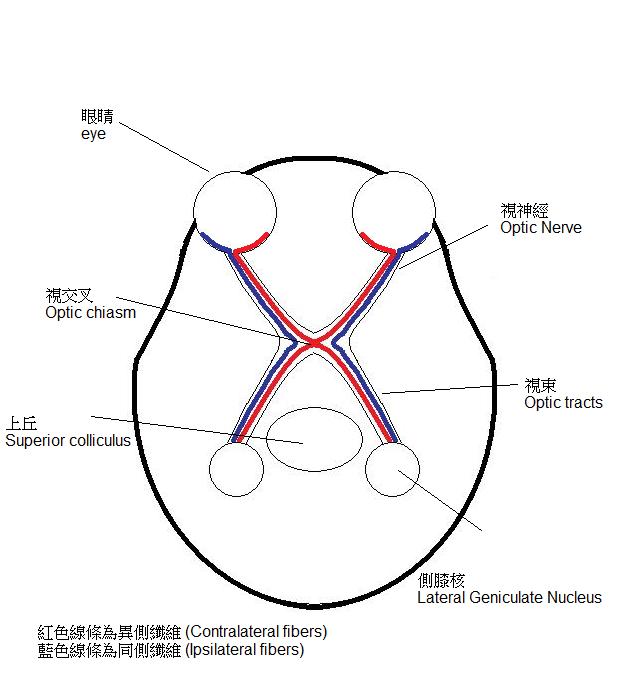
| + | * Optic Nerve 示意圖 | ||
| + | [[Image:OpticNervePicture.jpg]] | ||
| ** Optic Nerve(視神經) | ** Optic Nerve(視神經) | ||
| ** Optic chiasm(視交叉) | ** Optic chiasm(視交叉) | ||
| 第27行: | 第33行: | ||
| *** ipsilateral fibers(同側纖維) | *** ipsilateral fibers(同側纖維) | ||
| *** contralateral fibers (異側纖維) | *** contralateral fibers (異側纖維) | ||
| - | ** lateral projection | ||
| - | *** visual field(視野) | ||
| * Superior colliculus(上丘) | * Superior colliculus(上丘) | ||
| ** location | ** location | ||
| - | *** | + | *** top of brain stem(腦幹) |
| ** function | ** function | ||
| *** Multimodal(多感道) input | *** Multimodal(多感道) input | ||
| - | *** | + | *** control eye movement |
| ** receptive field property(特性) | ** receptive field property(特性) | ||
| - | *** lose center surround | + | ***lose center surround |
| ** Phylogenetic(系統發生) – old | ** Phylogenetic(系統發生) – old | ||
| - | *** | + | *** Visual center for lower animals |
| - | ***** 有receptive fields—but ill-defined ON OFF | + | ****Frog, fish.... |
| - | + | **In higher animals | |
| - | + | ***Superior colliculus的工作被visual cortex所取代 | |
| - | + | ***仍有的工作:Visual orienting | |
| - | **** | + | ****有receptive fields—but ill-defined ON OFF |
| + | ****對stimulus之where反應,what較不反應 | ||
| + | ***結果—guidance of eye movement | ||
| + | *Multisensory cells(多重感覺細胞) | ||
| + | **組成上丘的細胞除了接收視覺傳來的刺激外,還會接收聽覺傳來的刺激,因它可以接收不同的刺激,所以命名為多感覺細胞。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | *P.75 Figure4.2 | ||
| + | **a.LGN接受來自丘腦(thalamus;T)和其他LGN神經元(L)的訊號,興奮性突處說明L,抑制性突處則是T | ||
| + | **b.訊息經由LGN流入或流出,箭頭大小代表訊號大小 | ||
| + | *P.76 Figure4.3 | ||
| + | **LGN分六層, | ||
| + | 紅色層接收來自同側的訊號,藍色層接受來自對側的訊號 | ||
| * Lateral Geniculate Nucleus(側膝核) | * Lateral Geniculate Nucleus(側膝核) | ||
| - | ** | + | **Geniculate with bent knee |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| ** Magnocellular layers | ** Magnocellular layers | ||
| - | *** Layer 1,2 large-cell layers | ||
| - | *** Magnus Latin words mean『large』 | ||
| ** Parvocellular layers | ** Parvocellular layers | ||
| - | *** Layer 3,4,5,6 small-cell layers | ||
| - | *** Parvus Latin words mean 『small』 | ||
| ** K cells | ** K cells | ||
| - | * | + | *P.76 Figure4.4 |
| - | + | **杯上點A.B.C在視網膜形成A.B.C影像,也在側膝核(LGN)活化A.B.C,這個在LGN和視網膜相同的圖象說明LGN有視網膜的圖像 | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | ** | + | |
| * Maps in LGN | * Maps in LGN | ||
| 第69行: | 第73行: | ||
| ** retinotopic maps 中記錄的情況 | ** retinotopic maps 中記錄的情況 | ||
| - | * | + | *Structure of visual cortex |
| - | ** | + | **Primary visual cortex |
| - | ** | + | **V1 |
| - | ** | + | **Area 17 |
| - | ** | + | **Striate cortex |
| - | ** | + | ***1.5~2.0mm thick |
| - | * | + | ***100million cells in V1 each hemisphere |
| - | *** | + | ***6 layers |
| - | *** | + | ****Layer 4 input from LGN |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | **** input from | + | |
| - | + | === Retinal map === | |
| - | * | + | *Topographic |
| - | ** | + | **80% cells 處理 10%的visual field |
| - | + | ***因此在視野中心的東西在cortical level放大很大 | |
| - | + | ***週邊視野的東西則變小 | |
| - | *** | + | *Contralateral(對側) visual field |
| - | *** | + | **以visual field來分lateral projection |
| - | * | + | |
| - | ** | + | |
| - | * | + | *Receptive Fields of the Striate Cortex |
| - | ** | + | **Hubel and Wiesel 的1950年代末到1970中一連串的研究 |
| - | ** | + | **Hubel and Wiesel 1981年獲得Nobel prize |
| - | *** | + | ***The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1981 |
| - | *** | + | *Receptive Fields的形式《P.77 Figure4.6 |
| - | **** | + | **orientation |
| - | **** | + | **simple cortical cells |
| - | ** | + | *P.78 Figure4.7 |
| - | ** cortical | + | **Hubel and Wiesel當初發現的示意圖 |
| + | *到此的Receptive Field的特性 | ||
| + | **Retina Ganglion cell-> Center-surround LGN -> Center-surround | ||
| + | **Simple cortical -> bar with orientation | ||
| + | **Complex cortical -> direction of movement | ||
| + | **End-stopped cortical -> length of movement bar | ||
| - | * | + | *P.80 Figure4.9 |
| - | + | **Grating sti./ Contrast threshold | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | ** | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ==== Selective adaptation ==== | |
| - | * | + | *知覺研究者的微小電極 |
| - | * | + | *原理 |
| - | ** | + | **感覺神經如果有特異性(即針對特定的刺激才反應) |
| - | ** | + | **則長時間給于該刺激,則這個神經會疲勞(fatigue) |
| - | ** | + | **感覺神經疲勞,則其敏感度會下降,即絕對閾上升 |
| - | ** | + | **所以如果有刺激可以在長時間曝露下,讓我們對該刺激的絕對閾上升,可以推論我們內在感覺神經系統對該刺激有「特異性」 |
| - | * | + | *圖4.10 p.80之說明 |
| - | ** | + | **a. 先測量不同傾斜Grating偵測之threshold(是明暗對比的絕對閾,在閾限之下看起來是一片灰色) |
| + | **b. 曝露於高對比的Grating中(adaptation,適應過程) | ||
| + | **c. 適應之後,再量不同傾斜Grating偵測之threshold | ||
| + | *Selective adaptation之結果《P.81 Figure4.11 | ||
| - | * | + | ==== Selective Rearing ==== |
| - | ** | + | *選擇性飼養 |
| - | *** | + | **在特定(即只有限定品質)之環境下飼養動物 |
| - | ** | + | **目的在於測試環境對於動物影響 |
| + | **初生動物之感覺剥奪是最常用的 | ||
| + | **本例為:Blakemore and Cooper (1970)《P.81 Figure4.12 | ||
| - | * | + | === Maps in Striate Cortex === |
| - | ** | + | *大腦皮質部 |
| - | ** | + | **Columnar structure |
| - | ** | + | **功能上(似乎解剖上亦是)在皮質區有一類型的組織稱為柱狀組織(columnar structure) |
| - | ** | + | **同柱狀中之細胞功能類似 |
| - | *** | + | **不同柱狀間功能有差異 |
| - | ** | + | *研究方法 |
| + | **single cell recording (早期) | ||
| + | **brain imaging (近期) | ||
| - | * | + | *P.82 Figure4.13 |
| - | ** | + | **Hubel and Wiesel (1965)實驗結果 |
| - | + | *Cortical magnification factor《P.82 Figure 4.14 | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | * | + | *Brain Imaging 《P.83 Figure 4.15 |
| - | ** | + | **PET ( positron emission ) 正子電腦斷層掃描 |
| - | ** | + | **fMRI ( functional magnetic resonance imaging ) 功能性磁振造影 |
| - | ** | + | **方法 |
| - | *** | + | ***subtraction technique 減法! 《P.84 Figure 4.16 |
| - | * | + | *Retinotopic maps and Cortical magnification factor by brain imaging《P.84 Figure4.17 |
| - | *** | + | *Cortical magnification 示意圖《P.84 Figure4.18 |
| + | *Topographic map in cortex | ||
| + | *cortical magnification 實驗 | ||
| - | * | + | *Columnar Structure |
| - | ** | + | **Hubel and Wiesel 所整理 |
| - | *** | + | ***location column《P.84 Figure 4.19 |
| - | ** | + | ***orientation column《P.85 Figure 4.20 & 4.21 |
| - | * | + | ***ocular dominance column(單眼優勢) |
| - | *** | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | * | + | *Hubel and Wiesel之Hypercolumn《P.86 Figure4.22 |
| - | * | + | *color |
| - | ** | + | **blobs cell 泡泡細胞 |
| - | * | + | *Columns and hypercolumns |
| - | ** | + | **Hypercolumn by De Valois and De Valois |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | * | + | === Representation in V1 === |
| - | ** | + | *Representation |
| - | ** | + | **假想在各層次之資訊表達的方式 |
| - | ** | + | **亦可視為「計算過程」 |
| + | ***希望把資訊由硬體(大腦)獨立出來,即可由不同的硬體(如電腦)表現同質的東西 | ||
| + | **實際表現 | ||
| + | ***大腦神經興奮情況 | ||
| + | *Representation示意圖《P.87 Figure4.24 | ||
| + | *或許可能的腦內實際 《P.87 Figure4.25 | ||
| + | === Streams === | ||
| + | *Neural Pathway | ||
| + | **大腦中資訊流向 | ||
| + | **What, Where and How | ||
| + | *Dorsal pathway | ||
| + | **Where and How | ||
| + | *Ventral pathway | ||
| + | **What | ||
| + | *Brain Ablation《P.88 Figure4.26 | ||
| + | *Visual pathway《P.88 Figure4.27 | ||
| [[知覺心理學 | 回上頁]] | [[知覺心理學 | 回上頁]] | ||
當前修訂版本
目錄 |
[編輯] The Visual Cortex and Beyond
- Seeing as an active process
- 我們看東西是被動的嗎?
- 錯覺輪廓 illusory contour
- 差在那裡?
- 邊界傾斜
- 雙可圖形
- Rubin's vase
- 視覺解釋及記憶
- 你看到什麼課本最後也有解釋
- 前面四張圖的結論
- 我們所見不是只有光學影像本身
- 我們用眼睛及再加....來看
- 本章主題就是....
- ....是什麼?
- 我們看東西是被動的嗎?
[編輯] 今天講「腦」《P.74 Gigure4.1》
- 訊息自網膜節細胞離開視網膜
- 進入腦
- LGN -> visual cortex
- 視覺經驗
- Optic Nerve 示意圖
- Optic Nerve(視神經)
- Optic chiasm(視交叉)
- Optic tracts(視束)
- Nerve -> chiasm -> tracts
- 其實都是retina ganglion cells的axon
- 解剖上的不同
- lateral projection(側投射)
- 不是左眼到右腦
- ipsilateral fibers(同側纖維)
- contralateral fibers (異側纖維)
- Superior colliculus(上丘)
- location
- top of brain stem(腦幹)
- function
- Multimodal(多感道) input
- control eye movement
- receptive field property(特性)
- lose center surround
- Phylogenetic(系統發生) – old
- Visual center for lower animals
- Frog, fish....
- Visual center for lower animals
- In higher animals
- Superior colliculus的工作被visual cortex所取代
- 仍有的工作:Visual orienting
- 有receptive fields—but ill-defined ON OFF
- 對stimulus之where反應,what較不反應
- 結果—guidance of eye movement
- location
- Multisensory cells(多重感覺細胞)
- 組成上丘的細胞除了接收視覺傳來的刺激外,還會接收聽覺傳來的刺激,因它可以接收不同的刺激,所以命名為多感覺細胞。
- P.75 Figure4.2
- a.LGN接受來自丘腦(thalamus;T)和其他LGN神經元(L)的訊號,興奮性突處說明L,抑制性突處則是T
- b.訊息經由LGN流入或流出,箭頭大小代表訊號大小
- P.76 Figure4.3
- LGN分六層,
紅色層接收來自同側的訊號,藍色層接受來自對側的訊號
- Lateral Geniculate Nucleus(側膝核)
- Geniculate with bent knee
- Magnocellular layers
- Parvocellular layers
- K cells
- P.76 Figure4.4
- 杯上點A.B.C在視網膜形成A.B.C影像,也在側膝核(LGN)活化A.B.C,這個在LGN和視網膜相同的圖象說明LGN有視網膜的圖像
- Maps in LGN
- retinotopic map
- retinotopic maps 中記錄的情況
- Structure of visual cortex
- Primary visual cortex
- V1
- Area 17
- Striate cortex
- 1.5~2.0mm thick
- 100million cells in V1 each hemisphere
- 6 layers
- Layer 4 input from LGN
[編輯] Retinal map
- Topographic
- 80% cells 處理 10%的visual field
- 因此在視野中心的東西在cortical level放大很大
- 週邊視野的東西則變小
- 80% cells 處理 10%的visual field
- Contralateral(對側) visual field
- 以visual field來分lateral projection
- Receptive Fields of the Striate Cortex
- Hubel and Wiesel 的1950年代末到1970中一連串的研究
- Hubel and Wiesel 1981年獲得Nobel prize
- The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1981
- Receptive Fields的形式《P.77 Figure4.6
- orientation
- simple cortical cells
- P.78 Figure4.7
- Hubel and Wiesel當初發現的示意圖
- 到此的Receptive Field的特性
- Retina Ganglion cell-> Center-surround LGN -> Center-surround
- Simple cortical -> bar with orientation
- Complex cortical -> direction of movement
- End-stopped cortical -> length of movement bar
- P.80 Figure4.9
- Grating sti./ Contrast threshold
[編輯] Selective adaptation
- 知覺研究者的微小電極
- 原理
- 感覺神經如果有特異性(即針對特定的刺激才反應)
- 則長時間給于該刺激,則這個神經會疲勞(fatigue)
- 感覺神經疲勞,則其敏感度會下降,即絕對閾上升
- 所以如果有刺激可以在長時間曝露下,讓我們對該刺激的絕對閾上升,可以推論我們內在感覺神經系統對該刺激有「特異性」
- 圖4.10 p.80之說明
- a. 先測量不同傾斜Grating偵測之threshold(是明暗對比的絕對閾,在閾限之下看起來是一片灰色)
- b. 曝露於高對比的Grating中(adaptation,適應過程)
- c. 適應之後,再量不同傾斜Grating偵測之threshold
- Selective adaptation之結果《P.81 Figure4.11
[編輯] Selective Rearing
- 選擇性飼養
- 在特定(即只有限定品質)之環境下飼養動物
- 目的在於測試環境對於動物影響
- 初生動物之感覺剥奪是最常用的
- 本例為:Blakemore and Cooper (1970)《P.81 Figure4.12
[編輯] Maps in Striate Cortex
- 大腦皮質部
- Columnar structure
- 功能上(似乎解剖上亦是)在皮質區有一類型的組織稱為柱狀組織(columnar structure)
- 同柱狀中之細胞功能類似
- 不同柱狀間功能有差異
- 研究方法
- single cell recording (早期)
- brain imaging (近期)
- P.82 Figure4.13
- Hubel and Wiesel (1965)實驗結果
- Cortical magnification factor《P.82 Figure 4.14
- Brain Imaging 《P.83 Figure 4.15
- PET ( positron emission ) 正子電腦斷層掃描
- fMRI ( functional magnetic resonance imaging ) 功能性磁振造影
- 方法
- subtraction technique 減法! 《P.84 Figure 4.16
- Retinotopic maps and Cortical magnification factor by brain imaging《P.84 Figure4.17
- Cortical magnification 示意圖《P.84 Figure4.18
- Topographic map in cortex
- cortical magnification 實驗
- Columnar Structure
- Hubel and Wiesel 所整理
- location column《P.84 Figure 4.19
- orientation column《P.85 Figure 4.20 & 4.21
- ocular dominance column(單眼優勢)
- Hubel and Wiesel 所整理
- Hubel and Wiesel之Hypercolumn《P.86 Figure4.22
- color
- blobs cell 泡泡細胞
- Columns and hypercolumns
- Hypercolumn by De Valois and De Valois
[編輯] Representation in V1
- Representation
- 假想在各層次之資訊表達的方式
- 亦可視為「計算過程」
- 希望把資訊由硬體(大腦)獨立出來,即可由不同的硬體(如電腦)表現同質的東西
- 實際表現
- 大腦神經興奮情況
- Representation示意圖《P.87 Figure4.24
- 或許可能的腦內實際 《P.87 Figure4.25
[編輯] Streams
- Neural Pathway
- 大腦中資訊流向
- What, Where and How
- Dorsal pathway
- Where and How
- Ventral pathway
- What
- Brain Ablation《P.88 Figure4.26
- Visual pathway《P.88 Figure4.27